Acest articol vă va învăța despre o prezentare completă a utilizării buclei WHILE în SQL Server. A bucla WHILE este o instrucțiune de flux de control folosită pentru a executa în mod repetat setul de instrucțiuni până când condiția specificată este îndeplinită . Această buclă începe cu o condiție dată, evaluează-o și, dacă este TRUE, instrucțiunile vor intra în buclă pentru execuție ulterioară. Dacă condiția devine FALSĂ, nu va rula. Aceasta implică faptul că bucla while din SQL Server ar putea rula de zero sau de mai multe ori.
Organigrama buclei WHILE
Următoarea diagramă va explica fluxul de lucru complet al buclei WHILE din SQL Server:
panta nedefinita
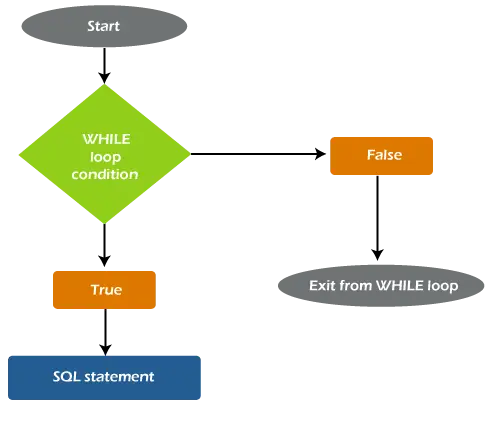
Putem vedea în această diagramă că condiția specificată este verificată pentru fiecare iterație și, pe baza rezultatului evaluării, se determină fluxul de cod. Dacă rezultatul este evaluat TRUE, fluxul de control intră în buclă pentru execuție ulterioară. Dacă rezultatul evaluat este FALS, fluxul de control va ieși din buclă și va fi executată orice instrucțiune sau interogare din afara buclei.
Sintaxă
Următoarea sintaxă ilustrează bucla WHILE din SQL Server:
WHILE boolean_condition BEGIN BREAK END;
În această sintaxă, avem următorii parametri sau argumente:
Exemplu de buclă WHILE
Să înțelegem cum funcționează bucla WHILE în SQL Server printr-un exemplu. În exemplul dat, am declarat mai întâi o valoare a tipul întreg și setați valoarea sa la 1. În continuare, bucla WHILE verifică starea și dacă este ADEVĂRAT , declarația de tipărire va fi tipărită. Când bucla devine FALS , următoarea instrucțiune după bucla WHILE va fi tipărită.
convertor șir în int
DECLARE @stud_value INT; SET @stud_value = 1; WHILE @stud_value <= 5 begin print 'mark henry'; set @stud_value="@stud_value" + 1; end; 'rose bennet'; < pre> <p>Executing this statement will return the following output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-2.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <p>In the above WHILE loop code snippet, we must increment the variable's value after each iteration. See the below part of the above code line as <strong>SET @stud_value = @stud_value + 1</strong> . If we do not write this statement, the loop will execute infinitely because it cannot becomes FALSE.</p> <pre> BEGIN PRINT 'Mark Henry'; SET @stud_value = @stud_value + 1; END; </pre> <h3>Infinite WHILE Loop</h3> <p>An infinite loop occurs when the evaluation of a condition will never be false. Therefore, the loop will never end and be executed forever. The loop in the following code snippet is infinite because the variable's value is not incremented.</p> <pre> DECLARE @stud_value INT; SET @stud_value = 1; WHILE @stud_value <= 5 begin print 'please stop execution!' end; < pre> <p>Executing the loop will display the below output. This loop will never end its execution until we do not cancel their execution of the query manually.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-3.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>Inserting Records with WHILE Loop</h3> <p>We can also use the WHILE loop to insert records into the defined table. Let us see how to inserts dummy records into the database. First, we will create a table named <strong>'bikeshop'</strong> containing three columns: <strong>Id, bike_name,</strong> and <strong>price</strong> . Execute the following statement to create this table:</p> <pre> CREATE TABLE bikeshop ( Id INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY, bike_name VARCHAR (50) NOT NULL, price FLOAT ) </pre> <p>Next, we will use the WHILE loop to insert ten records into this table by executing the following script:</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT; SET @count = 1; WHILE @count <= 10 begin insert into bikeshop values('bike-' + cast(@count as varchar), @count*5000) set @count="@count" 1; end; < pre> <p>In this code, we have declared a variable @ <strong>count</strong> and then initialize its value with 1 using a SET clause. Next, we have to define the loop body that executes the INSERT statement to add one record in each execution. The <strong>bike_name column</strong> will append the value of a @count variable with the string <strong>Bike</strong> , and the <strong>price</strong> column determines by the value of a @count variable multiplied by <strong>5000</strong> . The loop will execute until the value of the @count variable becomes FALSE. It means the WHILE loop will execute ten times and <strong>inserts ten records</strong> into the table bikeshop.</p> <p>Now, we can verify all the records of the bikeshop table with the SELECT statement. It will display the following output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-4.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>BREAK Statement</h3> <p>SQL Server also allows us to use the BREAK statement in the WHILE loop like programming languages. This statement is used to <strong>immediately stop the current iteration of the loop</strong> , and control flow resumes with the next statement after the loop. In general, we will use the <a href="/sql-server-if-else"> <strong>IF...ELSE statement</strong> </a> to check whether or not a condition has occurred.</p> <p>The following example will explain how to use the BREAK statement in the WHILE loop:</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT; SET @count = 1; WHILE @count = 6 BEGIN BREAK END SET @Count = @Count + 1 END; </pre> <p>Executing the code will display the below output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-5.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <p>The value of the variable is first evaluated in this code. If it is TRUE, the control enters into the loop and prints the statement. When the variable value is greater than or equal to 6, control enters the IF...ELSE block and executes the BREAK statement to terminate the loop. If an IF...ELSE block fails to meet the condition; then, the loop will keep running until the condition is changed to FALSE.</p> <h3>CONTINUE Statement</h3> <p>SQL Server also allows us to use the CONTINUE statement in the WHILE loop like programming languages. This statement immediately <strong>terminates the current execution of the loop when the specified condition is met</strong> , and control flow returns to the beginning of the loop. In general, the IF...ELSE statement will be used to test whether or not a condition has been met.</p> <p>The CONTINUE statement in the WHILE loop is demonstrated in the following example. In this example, we'll assume that we wish to use a WHILE loop to <strong>print only odd values</strong> . The CONTINUE statement can be used to do this. This example will first <strong>test</strong> whether the variable value is <strong>odd or even</strong> . If it is even, the execution goes inside the IF…ELSE statement blocks and decrement the variable value by one. Then, it will execute the CONTINUE statement and starts a new iteration from the beginning.</p> <pre> DECLARE @Count INT SET @Count = 1 WHILE (@Count <= 1 2="0" 44 20) begin if @count % set + continue end print 'the odd value is=" + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Count) SET @Count = @Count + 1 END </pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will display the below output:</p> <img src=" techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-6.webp' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>How to implementing paging with WHILE loop in SQL Server?</h3> <p>We can also use the WHILE loop for implementing the paging. Paging allows displaying the subset of records from a table at any particular time. The following example will explain this concept. The WHILE loop in the code will select two records from the bikeshop table at a time. The records that have been chosen are then displayed in the output.</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT DECLARE @limit INT; SET @count = 0 SET @limit = 2; WHILE @count <10 begin select * from bikeshop order by id offset @count rows fetch next @limit only set + 2; end; < pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will return the below output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-7.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>Nested WHILE Loop</h3> <p>The Nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server is simply a WHILE Loop written inside another WHILE Loop. When we work on multi-layered data, the Nested WHILE loops are essential. Because this concept is useful in extracting the layered data when we want to select them, it is recommended to be careful while using the nested loop.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax</strong> </p> <p>The following syntax illustrate the working of the nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server:</p> <pre> WHILE Expression BEGIN WHILE @Val2 <= 10 begin --second while loop statements sql end --this statement is outside the second --which first -- this < pre> <p>Let us explain this syntax step by step:</p> <p> <strong>Step 1:</strong> The loop starts by checking the first WHILE loop condition, and if it finds a false result, it will exit from While Loop. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution. This block will start the execution of the second WHILE loop. See step 2.</p> <p> <strong>Step 2:</strong> This step will check the condition in the Nested WHILE Loop, and if it is false, the second loop will be exit and execute the statement outside this. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution.</p> <p> <strong>Step 3:</strong> Once all the statements execute from the second WHILE loop, the control goes to the first WHILE and repeats the first step.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <p>The following example will print the multiplication table of 5 up to 10 using the nested WHILE loop.</p> <pre> DECLARE @val1 INT DECLARE @val2 INT SET @val1 = 5 SET @val2 = 1 WHILE @val1 <= 5 44 begin while @val2 <="10" print convert(varchar, @val1) + ' * @val2) techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-8.webp' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h2>Conclusion</h2> <p>The WHILE loop is a useful method when there is a need to execute a SQL script repeatedly. The article explained how to work with the WHILE loop in MS SQL Server to execute operations such as record insertion and pagination with a simple example. Here we have also learned the BREAK and CONTINUE statements to control the WHILE loop iteration.</p> <hr></=></pre></=></pre></10></pre></=></pre></=></pre></=></pre></=> Buclă WHILE infinită
O buclă infinită apare atunci când evaluarea unei condiții nu va fi niciodată falsă. Prin urmare, bucla nu se va termina niciodată și va fi executată pentru totdeauna. Bucla din următorul fragment de cod este infinită, deoarece valoarea variabilei nu este incrementată.
DECLARE @stud_value INT; SET @stud_value = 1; WHILE @stud_value <= 5 begin print \'please stop execution!\' end; < pre> <p>Executing the loop will display the below output. This loop will never end its execution until we do not cancel their execution of the query manually.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-3.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>Inserting Records with WHILE Loop</h3> <p>We can also use the WHILE loop to insert records into the defined table. Let us see how to inserts dummy records into the database. First, we will create a table named <strong>'bikeshop'</strong> containing three columns: <strong>Id, bike_name,</strong> and <strong>price</strong> . Execute the following statement to create this table:</p> <pre> CREATE TABLE bikeshop ( Id INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY, bike_name VARCHAR (50) NOT NULL, price FLOAT ) </pre> <p>Next, we will use the WHILE loop to insert ten records into this table by executing the following script:</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT; SET @count = 1; WHILE @count <= 10 begin insert into bikeshop values(\'bike-\' + cast(@count as varchar), @count*5000) set @count="@count" 1; end; < pre> <p>In this code, we have declared a variable @ <strong>count</strong> and then initialize its value with 1 using a SET clause. Next, we have to define the loop body that executes the INSERT statement to add one record in each execution. The <strong>bike_name column</strong> will append the value of a @count variable with the string <strong>Bike</strong> , and the <strong>price</strong> column determines by the value of a @count variable multiplied by <strong>5000</strong> . The loop will execute until the value of the @count variable becomes FALSE. It means the WHILE loop will execute ten times and <strong>inserts ten records</strong> into the table bikeshop.</p> <p>Now, we can verify all the records of the bikeshop table with the SELECT statement. It will display the following output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-4.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>BREAK Statement</h3> <p>SQL Server also allows us to use the BREAK statement in the WHILE loop like programming languages. This statement is used to <strong>immediately stop the current iteration of the loop</strong> , and control flow resumes with the next statement after the loop. In general, we will use the <a href="/sql-server-if-else"> <strong>IF...ELSE statement</strong> </a> to check whether or not a condition has occurred.</p> <p>The following example will explain how to use the BREAK statement in the WHILE loop:</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT; SET @count = 1; WHILE @count = 6 BEGIN BREAK END SET @Count = @Count + 1 END; </pre> <p>Executing the code will display the below output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-5.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <p>The value of the variable is first evaluated in this code. If it is TRUE, the control enters into the loop and prints the statement. When the variable value is greater than or equal to 6, control enters the IF...ELSE block and executes the BREAK statement to terminate the loop. If an IF...ELSE block fails to meet the condition; then, the loop will keep running until the condition is changed to FALSE.</p> <h3>CONTINUE Statement</h3> <p>SQL Server also allows us to use the CONTINUE statement in the WHILE loop like programming languages. This statement immediately <strong>terminates the current execution of the loop when the specified condition is met</strong> , and control flow returns to the beginning of the loop. In general, the IF...ELSE statement will be used to test whether or not a condition has been met.</p> <p>The CONTINUE statement in the WHILE loop is demonstrated in the following example. In this example, we'll assume that we wish to use a WHILE loop to <strong>print only odd values</strong> . The CONTINUE statement can be used to do this. This example will first <strong>test</strong> whether the variable value is <strong>odd or even</strong> . If it is even, the execution goes inside the IF…ELSE statement blocks and decrement the variable value by one. Then, it will execute the CONTINUE statement and starts a new iteration from the beginning.</p> <pre> DECLARE @Count INT SET @Count = 1 WHILE (@Count <= 1 2="0" 44 20) begin if @count % set + continue end print \'the odd value is=" + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Count) SET @Count = @Count + 1 END </pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will display the below output:</p> <img src=" techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-6.webp\' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>How to implementing paging with WHILE loop in SQL Server?</h3> <p>We can also use the WHILE loop for implementing the paging. Paging allows displaying the subset of records from a table at any particular time. The following example will explain this concept. The WHILE loop in the code will select two records from the bikeshop table at a time. The records that have been chosen are then displayed in the output.</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT DECLARE @limit INT; SET @count = 0 SET @limit = 2; WHILE @count <10 begin select * from bikeshop order by id offset @count rows fetch next @limit only set + 2; end; < pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will return the below output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-7.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>Nested WHILE Loop</h3> <p>The Nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server is simply a WHILE Loop written inside another WHILE Loop. When we work on multi-layered data, the Nested WHILE loops are essential. Because this concept is useful in extracting the layered data when we want to select them, it is recommended to be careful while using the nested loop.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax</strong> </p> <p>The following syntax illustrate the working of the nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server:</p> <pre> WHILE Expression BEGIN WHILE @Val2 <= 10 begin --second while loop statements sql end --this statement is outside the second --which first -- this < pre> <p>Let us explain this syntax step by step:</p> <p> <strong>Step 1:</strong> The loop starts by checking the first WHILE loop condition, and if it finds a false result, it will exit from While Loop. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution. This block will start the execution of the second WHILE loop. See step 2.</p> <p> <strong>Step 2:</strong> This step will check the condition in the Nested WHILE Loop, and if it is false, the second loop will be exit and execute the statement outside this. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution.</p> <p> <strong>Step 3:</strong> Once all the statements execute from the second WHILE loop, the control goes to the first WHILE and repeats the first step.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <p>The following example will print the multiplication table of 5 up to 10 using the nested WHILE loop.</p> <pre> DECLARE @val1 INT DECLARE @val2 INT SET @val1 = 5 SET @val2 = 1 WHILE @val1 <= 5 44 begin while @val2 <="10" print convert(varchar, @val1) + \' * @val2) techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-8.webp\' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h2>Conclusion</h2> <p>The WHILE loop is a useful method when there is a need to execute a SQL script repeatedly. The article explained how to work with the WHILE loop in MS SQL Server to execute operations such as record insertion and pagination with a simple example. Here we have also learned the BREAK and CONTINUE statements to control the WHILE loop iteration.</p> <hr></=></pre></=></pre></10></pre></=></pre></=></pre></=>
În continuare, vom folosi bucla WHILE pentru a insera zece înregistrări în acest tabel, executând următorul script:
DECLARE @count INT; SET @count = 1; WHILE @count <= 10 begin insert into bikeshop values(\'bike-\' + cast(@count as varchar), @count*5000) set @count="@count" 1; end; < pre> <p>In this code, we have declared a variable @ <strong>count</strong> and then initialize its value with 1 using a SET clause. Next, we have to define the loop body that executes the INSERT statement to add one record in each execution. The <strong>bike_name column</strong> will append the value of a @count variable with the string <strong>Bike</strong> , and the <strong>price</strong> column determines by the value of a @count variable multiplied by <strong>5000</strong> . The loop will execute until the value of the @count variable becomes FALSE. It means the WHILE loop will execute ten times and <strong>inserts ten records</strong> into the table bikeshop.</p> <p>Now, we can verify all the records of the bikeshop table with the SELECT statement. It will display the following output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-4.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>BREAK Statement</h3> <p>SQL Server also allows us to use the BREAK statement in the WHILE loop like programming languages. This statement is used to <strong>immediately stop the current iteration of the loop</strong> , and control flow resumes with the next statement after the loop. In general, we will use the <a href="/sql-server-if-else"> <strong>IF...ELSE statement</strong> </a> to check whether or not a condition has occurred.</p> <p>The following example will explain how to use the BREAK statement in the WHILE loop:</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT; SET @count = 1; WHILE @count = 6 BEGIN BREAK END SET @Count = @Count + 1 END; </pre> <p>Executing the code will display the below output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-5.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <p>The value of the variable is first evaluated in this code. If it is TRUE, the control enters into the loop and prints the statement. When the variable value is greater than or equal to 6, control enters the IF...ELSE block and executes the BREAK statement to terminate the loop. If an IF...ELSE block fails to meet the condition; then, the loop will keep running until the condition is changed to FALSE.</p> <h3>CONTINUE Statement</h3> <p>SQL Server also allows us to use the CONTINUE statement in the WHILE loop like programming languages. This statement immediately <strong>terminates the current execution of the loop when the specified condition is met</strong> , and control flow returns to the beginning of the loop. In general, the IF...ELSE statement will be used to test whether or not a condition has been met.</p> <p>The CONTINUE statement in the WHILE loop is demonstrated in the following example. In this example, we'll assume that we wish to use a WHILE loop to <strong>print only odd values</strong> . The CONTINUE statement can be used to do this. This example will first <strong>test</strong> whether the variable value is <strong>odd or even</strong> . If it is even, the execution goes inside the IF…ELSE statement blocks and decrement the variable value by one. Then, it will execute the CONTINUE statement and starts a new iteration from the beginning.</p> <pre> DECLARE @Count INT SET @Count = 1 WHILE (@Count <= 1 2="0" 44 20) begin if @count % set + continue end print \'the odd value is=" + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Count) SET @Count = @Count + 1 END </pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will display the below output:</p> <img src=" techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-6.webp\' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>How to implementing paging with WHILE loop in SQL Server?</h3> <p>We can also use the WHILE loop for implementing the paging. Paging allows displaying the subset of records from a table at any particular time. The following example will explain this concept. The WHILE loop in the code will select two records from the bikeshop table at a time. The records that have been chosen are then displayed in the output.</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT DECLARE @limit INT; SET @count = 0 SET @limit = 2; WHILE @count <10 begin select * from bikeshop order by id offset @count rows fetch next @limit only set + 2; end; < pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will return the below output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-7.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>Nested WHILE Loop</h3> <p>The Nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server is simply a WHILE Loop written inside another WHILE Loop. When we work on multi-layered data, the Nested WHILE loops are essential. Because this concept is useful in extracting the layered data when we want to select them, it is recommended to be careful while using the nested loop.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax</strong> </p> <p>The following syntax illustrate the working of the nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server:</p> <pre> WHILE Expression BEGIN WHILE @Val2 <= 10 begin --second while loop statements sql end --this statement is outside the second --which first -- this < pre> <p>Let us explain this syntax step by step:</p> <p> <strong>Step 1:</strong> The loop starts by checking the first WHILE loop condition, and if it finds a false result, it will exit from While Loop. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution. This block will start the execution of the second WHILE loop. See step 2.</p> <p> <strong>Step 2:</strong> This step will check the condition in the Nested WHILE Loop, and if it is false, the second loop will be exit and execute the statement outside this. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution.</p> <p> <strong>Step 3:</strong> Once all the statements execute from the second WHILE loop, the control goes to the first WHILE and repeats the first step.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <p>The following example will print the multiplication table of 5 up to 10 using the nested WHILE loop.</p> <pre> DECLARE @val1 INT DECLARE @val2 INT SET @val1 = 5 SET @val2 = 1 WHILE @val1 <= 5 44 begin while @val2 <="10" print convert(varchar, @val1) + \' * @val2) techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-8.webp\' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h2>Conclusion</h2> <p>The WHILE loop is a useful method when there is a need to execute a SQL script repeatedly. The article explained how to work with the WHILE loop in MS SQL Server to execute operations such as record insertion and pagination with a simple example. Here we have also learned the BREAK and CONTINUE statements to control the WHILE loop iteration.</p> <hr></=></pre></=></pre></10></pre></=></pre></=>
Executarea codului va afișa rezultatul de mai jos:

Valoarea variabilei este mai întâi evaluată în acest cod. Dacă este TRUE, controlul intră în buclă și tipărește declarația. Când valoarea variabilei este mai mare sau egală cu 6, controlul intră în blocul IF...ELSE și execută instrucțiunea BREAK pentru a termina bucla. Dacă un bloc IF...ELSE nu îndeplinește condiția; apoi, bucla va continua să ruleze până când condiția este schimbată în FALSE.
comenzi rapide linux
Declarație CONTINUE
SQL Server ne permite, de asemenea, să folosim instrucțiunea CONTINUE în bucla WHILE ca limbajele de programare. Această declarație imediat încheie execuția curentă a buclei atunci când condiția specificată este îndeplinită , iar fluxul de control revine la începutul buclei. În general, instrucțiunea IF...ELSE va fi folosită pentru a testa dacă a fost îndeplinită sau nu o condiție.
Instrucțiunea CONTINUE din bucla WHILE este demonstrată în exemplul următor. În acest exemplu, vom presupune că dorim să folosim o buclă WHILE pentru imprimați numai valori impare . Instrucțiunea CONTINUE poate fi folosită pentru a face acest lucru. Acest exemplu va fi mai întâi Test dacă valoarea variabilei este par sau impar . Dacă este par, execuția intră în blocurile de instrucțiuni IF...ELSE și decrește valoarea variabilei cu una. Apoi, va executa instrucțiunea CONTINUE și va începe o nouă iterație de la început.
DECLARE @Count INT SET @Count = 1 WHILE (@Count <= 1 2="0" 44 20) begin if @count % set + continue end print \'the odd value is=" + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Count) SET @Count = @Count + 1 END </pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will display the below output:</p> <img src=" techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-6.webp\' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>How to implementing paging with WHILE loop in SQL Server?</h3> <p>We can also use the WHILE loop for implementing the paging. Paging allows displaying the subset of records from a table at any particular time. The following example will explain this concept. The WHILE loop in the code will select two records from the bikeshop table at a time. The records that have been chosen are then displayed in the output.</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT DECLARE @limit INT; SET @count = 0 SET @limit = 2; WHILE @count <10 begin select * from bikeshop order by id offset @count rows fetch next @limit only set + 2; end; < pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will return the below output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-7.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>Nested WHILE Loop</h3> <p>The Nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server is simply a WHILE Loop written inside another WHILE Loop. When we work on multi-layered data, the Nested WHILE loops are essential. Because this concept is useful in extracting the layered data when we want to select them, it is recommended to be careful while using the nested loop.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax</strong> </p> <p>The following syntax illustrate the working of the nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server:</p> <pre> WHILE Expression BEGIN WHILE @Val2 <= 10 begin --second while loop statements sql end --this statement is outside the second --which first -- this < pre> <p>Let us explain this syntax step by step:</p> <p> <strong>Step 1:</strong> The loop starts by checking the first WHILE loop condition, and if it finds a false result, it will exit from While Loop. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution. This block will start the execution of the second WHILE loop. See step 2.</p> <p> <strong>Step 2:</strong> This step will check the condition in the Nested WHILE Loop, and if it is false, the second loop will be exit and execute the statement outside this. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution.</p> <p> <strong>Step 3:</strong> Once all the statements execute from the second WHILE loop, the control goes to the first WHILE and repeats the first step.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <p>The following example will print the multiplication table of 5 up to 10 using the nested WHILE loop.</p> <pre> DECLARE @val1 INT DECLARE @val2 INT SET @val1 = 5 SET @val2 = 1 WHILE @val1 <= 5 44 begin while @val2 <="10" print convert(varchar, @val1) + \' * @val2) techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-8.webp\' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h2>Conclusion</h2> <p>The WHILE loop is a useful method when there is a need to execute a SQL script repeatedly. The article explained how to work with the WHILE loop in MS SQL Server to execute operations such as record insertion and pagination with a simple example. Here we have also learned the BREAK and CONTINUE statements to control the WHILE loop iteration.</p> <hr></=></pre></=></pre></10></pre></=>
