Luarea deciziilor este cel mai important aspect al aproape tuturor limbajelor de programare. După cum sugerează și numele, luarea deciziilor ne permite să rulăm un anumit bloc de cod pentru o anumită decizie. Aici, deciziile sunt luate cu privire la valabilitatea condițiilor particulare. Verificarea condiției este coloana vertebrală a luării deciziilor.
comentarii java
În python, luarea deciziilor este efectuată de următoarele afirmații.
| Afirmație | Descriere |
|---|---|
| If Statement | Declarația if este folosită pentru a testa o anumită condiție. Dacă condiția este adevărată, va fi executat un bloc de cod (if-block). |
| If - else Declarație | Instrucțiunea if-else este similară cu instrucțiunea if, cu excepția faptului că, oferă și blocul codului pentru cazul fals al condiției de verificat. Dacă condiția furnizată în instrucțiunea if este falsă, atunci instrucțiunea else va fi executată. |
| Imbricat if Declarație | Instrucțiunile imbricate if ne permit să folosim if ? declarația else în interiorul unei declarații if exterioare. |
Indentare în Python
Pentru ușurința programării și pentru a obține simplitate, python nu permite utilizarea parantezelor pentru codul la nivel de bloc. În Python, indentarea este folosită pentru a declara un bloc. Dacă două instrucțiuni sunt la același nivel de indentare, atunci ele fac parte din același bloc.
În general, sunt date patru spații pentru a indenta instrucțiunile care sunt o cantitate tipică de indentare în python.
Indentarea este cea mai utilizată parte a limbajului Python, deoarece declară blocul de cod. Toate instrucțiunile unui bloc sunt destinate la același nivel de indentare. Vom vedea cum are loc indentarea reală în luarea deciziilor și alte lucruri în python.
Declarația if
Instrucțiunea if este folosită pentru a testa o anumită condiție și dacă condiția este adevărată, execută un bloc de cod cunoscut sub numele de if-block. Condiția declarației if poate fi orice expresie logică validă care poate fi fie evaluată la adevărat, fie la fals.
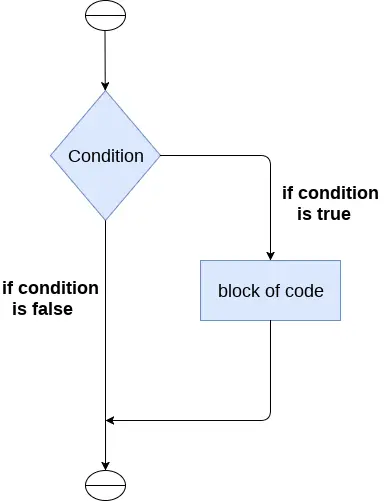
Sintaxa instrucțiunii if este dată mai jos.
if expression: statement
Exemplul 1
# Simple Python program to understand the if statement num = int(input('enter the number:')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if num%2 == 0: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The Given number is an even number')
Ieșire:
enter the number: 10 The Given number is an even number
Exemplul 2: Program pentru a tipări cel mai mare dintre cele trei numere.
# Simple Python Program to print the largest of the three numbers. a = int (input('Enter a: ')); b = int (input('Enter b: ')); c = int (input('Enter c: ')); if a>b and a>c: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given a is largest'); if b>a and b>c: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given b is largest'); if c>a and c>b: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given c is largest');
Ieșire:
Enter a: 100 Enter b: 120 Enter c: 130 From the above three numbers given c is largest
Declarația dacă-altfel
Instrucțiunea if-else oferă un bloc else combinat cu instrucțiunea if care este executată în cazul fals al condiției.
Dacă condiția este adevărată, atunci blocul if este executat. În caz contrar, blocul else este executat.

Sintaxa instrucțiunii if-else este dată mai jos.
operator condițional în java
if condition: #block of statements else: #another block of statements (else-block)
Exemplul 1: Program pentru a verifica dacă o persoană este eligibilă pentru vot sau nu.
# Simple Python Program to check whether a person is eligible to vote or not. age = int (input('Enter your age: ')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if age>=18: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('You are eligible to vote !!'); else: print('Sorry! you have to wait !!');
Ieșire:
Enter your age: 90 You are eligible to vote !!
Exemplul 2: Program pentru a verifica dacă un număr este par sau nu.
# Simple Python Program to check whether a number is even or not. num = int(input('enter the number:')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if num%2 == 0: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The Given number is an even number') else: print('The Given Number is an odd number')
Ieșire:
enter the number: 10 The Given number is even number
Declarația elif
Instrucțiunea elif ne permite să verificăm mai multe condiții și să executăm blocul specific de instrucțiuni în funcție de condiția adevărată dintre ele. Putem avea orice număr de declarații elif în programul nostru, în funcție de nevoile noastre. Cu toate acestea, utilizarea elif este opțională.
Instrucțiunea elif funcționează ca o instrucțiune ladder if-else-if în C. Trebuie să fie urmată de o instrucțiune if.
Sintaxa instrucțiunii elif este dată mai jos.
înlocuiți șirul în șirul de caractere java
if expression 1: # block of statements elif expression 2: # block of statements elif expression 3: # block of statements else: # block of statements

Exemplul 1
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement number = int(input('Enter the number?')) # Here, we are taking an integer number and taking input dynamically if number==10: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equals to 10') elif number==50: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equal to 50'); elif number==100: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equal to 100'); else: print('The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100');
Ieșire:
Enter the number?15 The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
Exemplul 2
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement marks = int(input('Enter the marks? ')) # Here, we are taking an integer marks and taking input dynamically if marks > 85 and marks 60 and marks 40 and marks 30 and marks <= 40): # here, we are checking the condition. if condition is true, will enter block print('you scored grade c ...') else: print('sorry you fail ?') < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter the marks? 89 Congrats ! you scored grade A ... </pre> <hr></=> 