Dată o hârtie dreptunghiulară de dimensiuni a x b . Sarcina este să tăiați întreaga hârtie în minim număr de pătrat bucăți. Putem alege bucăți pătrate de orice dimensiune dar trebuie tăiate fără a se suprapune sau a lăsa spațiu suplimentar .
Exemple:
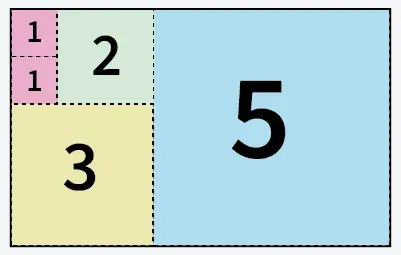
Intrare: a = 5 b = 8
5 pătrate tăiate din hârtie de dimensiune 5 X 8
Ieșire: 5
Explicaţie: Putem tăia hârtia în 5 pătrate: 1 pătrat de dimensiunea 5x5 1 pătrat de dimensiunea 3x3 1 pătrat de dimensiunea 2x2 și 2 pătrate de dimensiunea 1x1.Intrare: a = 13 b = 11
6 pătrate tăiate din hârtie de dimensiunea 13 X 11
Ieșire: 6
Explicaţie: Putem tăia hârtia în 6 pătrate: 1 pătrat de dimensiunea 7x7 1 pătrat de dimensiunea 6x6 1 pătrat de dimensiunea 5x5 2 pătrate de dimensiunea 4x4 și 1 pătrat de dimensiunea 1x1.Intrare: a = 6 b = 7
5 pătrate tăiate din hârtie de dimensiune 6 X 7
Ieșire: 5
Explicaţie: Putem tăia hârtia în 5 pătrate: 1 pătrat de dimensiunea 4x4 2 pătrate de dimensiunea 3x3 și 2 pătrate de dimensiunea 3x3.
Cuprins
- [Abordare incorectă 1] Folosind tehnica Greedy
- [Abordare incorectă 2] Folosind programarea dinamică
- [Abordare corectă] Folosind DFS și programare dinamică
[Abordare incorectă 1] Folosind tehnica Greedy
La prima vedere s-ar putea părea că problema poate fi rezolvată cu ușurință prin tăierea celui mai mare pătrat posibil din hârtie, urmată de tăierea celui mai mare pătrat din hârtie rămasă și așa mai departe până când am tăiat întreaga hârtie. Dar această soluție este incorectă.
De ce Greedy Approach nu va funcționa?
Luați în considerare o hârtie de dimensiune 6x7 atunci dacă încercăm să tăiem hârtia cu lăcomie vom obține 7 pătrate: 1 pătrat de dimensiune 6x6 și 6 pătrate de dimensiune 1x1 întrucât soluția corectă este: 5. Prin urmare, abordarea lacomă nu va funcționa.
[Abordare incorectă 2] Folosind programarea dinamică
Programare dinamică cu tăieturi verticale sau orizontale: O altă soluție care ar putea părea corectă este utilizarea Programare dinamică . Putem menține un tabel dp[][] astfel încât dp[i][j] = numărul minim de pătrate care pot fi tăiate din hârtie de dimensiune eu x j . Apoi pentru hârtie de dimensiune axb
- Putem încerca să o tăiem de-a lungul fiecărui rând: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) unde k poate fi în intervalul [1 i - 1].
- Putem încerca să o tăiem de-a lungul fiecărei coloane: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) unde k poate fi în intervalul [1 j - 1].
În cele din urmă, minimul tuturor tăierilor va fi răspunsul. Dar și această soluție este incorectă.
De ce tăierea verticală sau orizontală cu Abordarea de programare dinamică nu va funcționa?
Acest lucru nu va funcționa, deoarece presupunem că o tăietură verticală sau orizontală va împărți întotdeauna dreptunghiul în două părți. Luați în considerare o hârtie de dimensiune 13x11 atunci dacă încercăm să tăiem hârtia folosind abordarea DP, vom obține 8 pătrate, dar răspunsul corect (așa cum se arată în exemple) este 6. Prin urmare, programarea dinamică nu va funcționa.
[Abordare corectă] Folosind DFS și programare dinamică
C++The idee este să tăiați întreaga hârtie folosind DFS în de jos în sus mod. La fiecare pas, găsiți colțul cel mai jos din stânga al hârtiei și încercați să tăiați pătrate de toate dimensiunile posibile din acel colț. După ce tăiați un pătrat, găsiți din nou colțul din stânga jos al hârtiei rămase pentru a tăia pătrate de toate dimensiunile posibile și așa mai departe. Dar dacă încercăm toate tăieturile posibile din colțul din stânga cel mai jos al fiecărei dimensiuni posibile de hârtie, atunci ar fi destul de ineficient. Îl putem optimiza utilizând Programare dinamică pentru a stoca tăieturi minime pentru fiecare dimensiune posibilă de hârtie.
Pentru a identifica în mod unic orice dimensiune de hârtie, putem menține o matrice remSq[] astfel încât remSq[i] stochează numărul de pătrate rămase de dimensiunea 1x1 în coloana a I-a a hârtiei. Deci, pentru o hârtie de dimensiunea 6x7 remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. De asemenea, pentru a găsi colțul din stânga cel mai jos vom găsi primul indice care are pătratele maxime rămase. Deci, putem calcula valoarea remSq[] array pentru a găsi o cheie unică pentru toate valorile posibile ale remSq[] array.
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include
// Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.*; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int base = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Map<Integer Integer> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key); int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = Arrays.copyOf(remSq b); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo.put(key ans); return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; Arrays.fill(remSq a); Map<Integer Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System.out.println(minCut(a b)); } }
# Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey(remSq b): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range(b): key += remSq[i] * base base = base * (b + 1) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil(remSq a b memo): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey(remSq b) if key in memo: return memo[key] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range(b): if remSq[i] > maxRemSq: maxRemSq = remSq[i] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0: return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq[:] ans = float('inf') # Find the ending point of min height while end < b: # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq or newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0: break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range(start end + 1): newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)) end += 1 memo[key] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut(a b): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b: return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [a] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print(minCut(a b))
// C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int baseVal = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * baseVal); baseVal = baseVal * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Dictionary<int int> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.ContainsKey(key)) return memo[key]; int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = (int[])remSq.Clone(); int ans = int.MaxValue; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.Min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) remSq[i] = a; Dictionary<int int> memo = new Dictionary<int int>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } static void Main() { int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console.WriteLine(minCut(a b)); } }
// JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey(remSq b) { let base = 1; let key = 0; for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey(remSq b); if (key in memo) return memo[key]; let maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq === 0) return 0; end = start; let newRemSq = remSq.slice(); let ans = Infinity; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut(a b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a === b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array(b).fill(a); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console.log(minCut(a b));
Ieșire
6
Complexitatea timpului: O(a^b) pentru fiecare dintre b coloane putem avea câte un pătrat.
Spațiu auxiliar: O(a^b) datorită memorizării care stochează fiecare stare unică.

 5 pătrate tăiate din hârtie de dimensiune 5 X 8
5 pătrate tăiate din hârtie de dimensiune 5 X 8 6 pătrate tăiate din hârtie de dimensiunea 13 X 11
6 pătrate tăiate din hârtie de dimensiunea 13 X 11 5 pătrate tăiate din hârtie de dimensiune 6 X 7
5 pătrate tăiate din hârtie de dimensiune 6 X 7