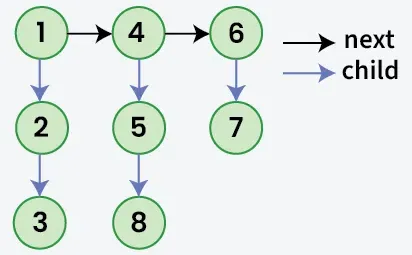
Dată o listă legată unde, în plus față de Următorul pointer fiecare nod are un copil indicator care poate indica sau nu o listă separată. Aceste liste de copii pot avea una sau mai multe copiii lor să producă a pe mai multe niveluri lista legată. Având în vedere cap al primul nivel a listei. Sarcina este să aplatiza lista astfel încât toate nodurile să apară în a cu un singur nivel lista legată. Aplatizați lista într-un mod în care toate nodurile de la primul nivel ar trebui să vină primul apoi noduri ale doilea nivel și așa mai departe.
Exemple:
Intrare:
Ieșire: 1->4->6->2->5->7->3->8
Explicaţie: Lista legată pe mai multe niveluri este aplatizată deoarece nu are pointeri copii.
Am discutat aplatizarea unei liste legate pe mai multe niveluri unde nodurile au doi pointeri în jos și următor. În postarea anterioară noi turtit lista legată nivel înțelept. Cum să aplatizam o listă legată atunci când trebuie să procesăm întotdeauna indicatorul în jos înainte de următorul la fiecare nod.
Cuprins
- [Abordare așteptată] Utilizarea recursiunii - O(n) Timp și O(n) Spațiu
- [Abordare alternativă] Folosind Stack - O(n) Timp și O(n) Spațiu
[Abordare așteptată] Utilizarea recursiunii - O(n) Timp și O(n) Spațiu
C++Abordarea este de a recursiv aplatiza a conectat pe mai multe niveluri lista prin parcurgerea fiecărui nod și a nodurilor sale fii. Primul aplatiza lista de copii folosind recursiunea. Odată ce lista de copii este aplatizată, treceți la nodul următor în succesiune. În timpul traversării menţineţi a referinţă la nod vizitat anterior și conectați-l la nodul curent. Acest proces asigură că toate nodurile de la diferite niveluri sunt conectate într-un o singură listă liniară păstrând în același timp ordinea în profunzime.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise #include
// A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { int data; Node next down; Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void flattenList(Node curr Node[] prev) { if (curr == null) return; // Add the current element to the list. if (prev[0] != null) prev[0].next = curr; prev[0] = curr; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr.next; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList(curr.down prev); // Recursively add the next list flattenList(next prev); } static void printList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { System.out.print(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); Node[] prev = new Node[1]; flattenList(head prev); printList(head); } }
# A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.next = None self.down = None def flatten_list(curr prev): if curr is None: return # Add the current element to the list. if prev[0] is not None: prev[0].next = curr prev[0] = curr # Store the next pointer next_node = curr.next # Recursively add the bottom list flatten_list(curr.down prev) # Recursively add the next list flatten_list(next_node prev) def print_list(head): curr = head while curr is not None: print(curr.data end=' ') curr = curr.next print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node(5) head.down = Node(7) head.down.down = Node(8) head.down.down.down = Node(30) head.next = Node(10) head.next.next = Node(19) head.next.next.down = Node(22) head.next.next.down.down = Node(50) head.next.next.next = Node(28) prev = [None] flatten_list(head prev) print_list(head)
// A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next down; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList(Node curr ref Node prev) { if (curr == null) return; // Add the current element to the list. if (prev != null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr.next; // Recursively add the bottom list FlattenList(curr.down ref prev); // Recursively add the next list FlattenList(next ref prev); } static void PrintList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Console.Write(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); Node prev = null; FlattenList(head ref prev); PrintList(head); } }
// A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; this.down = null; } } function flattenList(curr prev) { if (curr === null) return; // Add the current element to the list. if (prev[0] !== null) prev[0].next = curr; prev[0] = curr; // Store the next pointer let next = curr.next; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList(curr.down prev); // Recursively add the next list flattenList(next prev); } function printList(head) { let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { console.log(curr.data); curr = curr.next; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); let prev = [null]; flattenList(head prev); printList(head);
Ieșire
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28
[Abordare alternativă] Folosind Stack - O(n) Timp și O(n) Spațiu
C++Abordarea este de a traversa listă legată pe mai multe niveluri folosind a stivă . Începe prin împingând cel nodul cap pe stivă. Apoi, în timp ce stiva nu este goală pop nodul superior și procesați-l. Pentru fiecare nod Apăsaţi sale indicatori următor și în jos (dacă există) pe stivă. În timpul acestui proces legați nodul curent la nodul anterior menținerea listei într-o formă aplatizată. Traversarea asigură că nodurile de la toate nivelurile sunt conectate într-un listă legată cu un singur nivel păstrând ordinea în profunzime.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack #include
// A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack import java.util.Stack; class Node { int data; Node next down; Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void flattenList(Node head) { if (head == null) return; Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(head); Node prev = null; while (!stack.isEmpty()) { Node curr = stack.pop(); // Push the next node first if (curr.next != null) stack.push(curr.next); // Push the bottom node into stack if (curr.down != null) stack.push(curr.down); // Add the current element to the list if (prev != null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; } } static void printList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { System.out.print(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); flattenList(head); printList(head); } }
# A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise using stack class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.next = None self.down = None def flatten_list(head): if head is None: return stack = [head] prev = None while stack: curr = stack.pop() # Push the next node first if curr.next: stack.append(curr.next) # Push the bottom node into stack if curr.down: stack.append(curr.down) # Add the current element to the list if prev: prev.next = curr prev = curr def print_list(head): curr = head while curr: print(curr.data end=' ') curr = curr.next print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node(5) head.down = Node(7) head.down.down = Node(8) head.down.down.down = Node(30) head.next = Node(10) head.next.next = Node(19) head.next.next.down = Node(22) head.next.next.down.down = Node(50) head.next.next.next = Node(28) flatten_list(head) print_list(head)
// A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node next down; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList(Node head) { if (head == null) return; Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); stack.Push(head); Node prev = null; while (stack.Count > 0) { Node curr = stack.Pop(); // Push the next node first if (curr.next != null) stack.Push(curr.next); // Push the bottom node into stack if (curr.down != null) stack.Push(curr.down); // Add the current element to the list if (prev != null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; } } static void PrintList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Console.Write(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); FlattenList(head); PrintList(head); } }
// A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; this.down = null; } } function flattenList(head) { if (head === null) return; let stack = [head]; let prev = null; while (stack.length > 0) { let curr = stack.pop(); // Push the next node first if (curr.next !== null) stack.push(curr.next); // Push the bottom node into stack if (curr.down !== null) stack.push(curr.down); // Add the current element to the list if (prev !== null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; } } function printList(head) { let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { console.log(curr.data); curr = curr.next; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); flattenList(head); printList(head);
Ieșire
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28