The asList() Metodă de java.util.Arrays clasa este folosită pentru a returna o listă de dimensiuni fixe susținută de matricea specificată. Această metodă acționează ca a punte între API-urile bazate pe matrice și cele bazate pe colecții , în combinație cu Collection.toArray(). Lista returnată este serializabilă și implementează RandomAccess.
Bacsis: Aceasta rulează în timp O(1).
Sintaxă:
public static List asList(T... a)>
Parametri: Această metodă ia matrice a care trebuie convertit într-o Listă. Aici... este cunoscut ca vararg care este o matrice de parametri și funcționează similar cu un parametru de matrice de obiecte.
Notă specială: Tipul de matrice trebuie să fie o clasă Wrapper (Integer, Float, etc) în cazul tipurilor de date primitive (int, float, etc), adică nu puteți trece int a[], dar puteți trece Integer a[]. Dacă transmiteți int a[], această funcție va returna o listă și nu o listă, deoarece autoboxing-ul nu se întâmplă în acest caz și int a[] este el însuși identificat ca un obiect și va fi returnat un tablou List of int, în loc de listă. de numere întregi, care vor da eroare în diferite funcții de colectare.
Valoare returnată: Această metodă returnează a vizualizare listă a matricei specificate.
Exemplul 1:
natasha dalal
Java
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class for a string value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of String type> >String a[]> >=>new> String[] {>'A'>,>'B'>,>'C'>,>'D'> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements in list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statement> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Ieșire
subșir șir
The list is: [A, B, C, D]>
Exemplul 2:
Java
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class For an integer value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements inside list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statements> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Ieșire
The list is: [10, 20, 30, 40]>
Exemplul 3:
java altfel dacă
Java
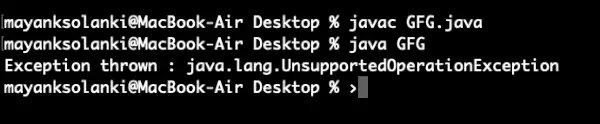
// Java Program to demonstrate asList() method> // Which returns fixed size list and> // throws UnsupportedOperationException> // if any element is added using add() method> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Adding another int to the list> >// As Arrays.asList() returns fixed size> >// list, we'll get> >// java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException> >list.add(>50>);> >// Printing all the elements of list> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (UnsupportedOperationException e) {> >// Display message when exception occurs> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>
Ieșire: