În acest articol, vom discuta despre algoritmul Quicksort. Procedura de lucru a Quicksort este, de asemenea, simplă. Acest articol va fi foarte util și interesant pentru studenți, deoarece s-ar putea confrunta cu sortarea rapidă ca întrebare în examenele lor. Deci, este important să discutăm subiectul.
Sortarea este o modalitate de aranjare a articolelor într-o manieră sistematică. Quicksort este algoritmul de sortare utilizat pe scară largă care face n jurnal n comparații în caz mediu pentru sortarea unui tablou de n elemente. Este un algoritm de sortare mai rapid și foarte eficient. Acest algoritm urmează abordarea împărțiți și cuceriți. Divide and conquer este o tehnică de descompunere a algoritmilor în subprobleme, apoi de rezolvare a subproblemelor și de a combina rezultatele înapoi pentru a rezolva problema inițială.
sistem de operare linux
Divide: În Divide, alegeți mai întâi un element pivot. După aceea, împărțiți sau rearanjați matricea în două sub-matrice astfel încât fiecare element din sub-matricea din stânga să fie mai mic sau egal cu elementul pivot și fiecare element din sub-matricea din dreapta să fie mai mare decât elementul pivot.
A cuceri: Recursiv, sortați două subbary cu Quicksort.
Combina: Combinați matricea deja sortată.
Quicksort alege un element ca pivot, apoi partiţionează matricea dată în jurul elementului pivot ales. În sortarea rapidă, o matrice mare este împărțită în două matrice în care una deține valori care sunt mai mici decât valoarea specificată (Pivot), iar o altă matrice deține valorile care sunt mai mari decât pivotul.
După aceea, sub-matricele din stânga și din dreapta sunt, de asemenea, partiționate folosind aceeași abordare. Va continua până când singurul element rămâne în sub-matrice.
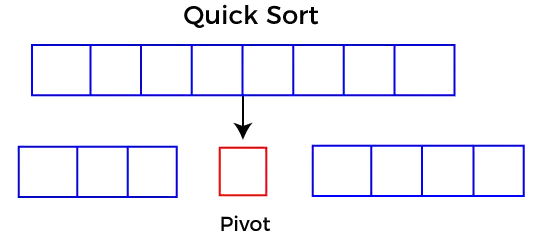
Alegerea pivotului
Alegerea unui pivot bun este necesară pentru implementarea rapidă a sortării rapide. Cu toate acestea, este tipic să se determine un pivot bun. Unele dintre modalitățile de a alege un pivot sunt următoarele:
- Pivotul poate fi aleatoriu, adică selectați pivotul aleatoriu din matricea dată.
- Pivot poate fi fie elementul din dreapta al elementului din stânga al matricei date.
- Selectați mediana ca element pivot.
Algoritm
Algoritm:
QUICKSORT (array A, start, end) { 1 if (start <end) 2 3 4 5 6 { p="partition(A," start, end) quicksort (a, - 1) + 1, } < pre> <p> <strong>Partition Algorithm:</strong> </p> <p>The partition algorithm rearranges the sub-arrays in a place.</p> <pre> PARTITION (array A, start, end) { 1 pivot ? A[end] 2 i ? start-1 3 for j ? start to end -1 { 4 do if (A[j] <pivot) 1 5 6 7 8 9 { then i ? + swap a[i] with a[j] }} a[i+1] a[end] return i+1 } < pre> <h2>Working of Quick Sort Algorithm</h2> <p>Now, let's see the working of the Quicksort Algorithm.</p> <p>To understand the working of quick sort, let's take an unsorted array. It will make the concept more clear and understandable.</p> <p>Let the elements of array are -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-2.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>In the given array, we consider the leftmost element as pivot. So, in this case, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 27 and a[pivot] = 24.</p> <p>Since, pivot is at left, so algorithm starts from right and move towards left.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-3.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] <a[right], so algorithm moves forward one position towards left, i.e. -< p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-4.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 19, and a[pivot] = 24.</p> <p>Because, a[pivot] > a[right], so, algorithm will swap a[pivot] with a[right], and pivot moves to right, as -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-5.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 19, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. Since, pivot is at right, so algorithm starts from left and moves to right.</p> <p>As a[pivot] > a[left], so algorithm moves one position to right as -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-6.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 9, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] > a[left], so algorithm moves one position to right as -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-7.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 29, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] <a[left], so, swap a[pivot] and a[left], now pivot is at left, i.e. -< p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-8.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Since, pivot is at left, so algorithm starts from right, and move to left. Now, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 29, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] <a[right], so algorithm moves one position to left, as -< p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-9.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 24, and a[right] = 14. As a[pivot] > a[right], so, swap a[pivot] and a[right], now pivot is at right, i.e. -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-10.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 14, and a[right] = 24. Pivot is at right, so the algorithm starts from left and move to right.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-11.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 24, and a[right] = 24. So, pivot, left and right are pointing the same element. It represents the termination of procedure.</p> <p>Element 24, which is the pivot element is placed at its exact position.</p> <p>Elements that are right side of element 24 are greater than it, and the elements that are left side of element 24 are smaller than it.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-12.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, in a similar manner, quick sort algorithm is separately applied to the left and right sub-arrays. After sorting gets done, the array will be -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-13.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <h2>Quicksort complexity</h2> <p>Now, let's see the time complexity of quicksort in best case, average case, and in worst case. We will also see the space complexity of quicksort.</p> <h3>1. Time Complexity</h3> <table class="table"> <tr> <th>Case</th> <th>Time Complexity</th> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Best Case</strong> </td> <td>O(n*logn)</td> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Average Case</strong> </td> <td>O(n*logn)</td> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Worst Case</strong> </td> <td>O(n<sup>2</sup>)</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <tr><td>Best Case Complexity -</td> In Quicksort, the best-case occurs when the pivot element is the middle element or near to the middle element. The best-case time complexity of quicksort is <strong>O(n*logn)</strong> . </tr><tr><td>Average Case Complexity -</td> It occurs when the array elements are in jumbled order that is not properly ascending and not properly descending. The average case time complexity of quicksort is <strong>O(n*logn)</strong> . </tr><tr><td>Worst Case Complexity -</td> In quick sort, worst case occurs when the pivot element is either greatest or smallest element. Suppose, if the pivot element is always the last element of the array, the worst case would occur when the given array is sorted already in ascending or descending order. The worst-case time complexity of quicksort is <strong>O(n<sup>2</sup>)</strong> . </tr></ul> <p>Though the worst-case complexity of quicksort is more than other sorting algorithms such as <strong>Merge sort</strong> and <strong>Heap sort</strong> , still it is faster in practice. Worst case in quick sort rarely occurs because by changing the choice of pivot, it can be implemented in different ways. Worst case in quicksort can be avoided by choosing the right pivot element.</p> <h3>2. Space Complexity</h3> <table class="table"> <tr> <td> <strong>Space Complexity</strong> </td> <td>O(n*logn)</td> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Stable</strong> </td> <td>NO</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <li>The space complexity of quicksort is O(n*logn).</li> </ul> <h2>Implementation of quicksort</h2> <p>Now, let's see the programs of quicksort in different programming languages.</p> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quicksort in C language.</p> <pre> #include /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ int partition (int a[], int start, int end) { int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element int i = (start - 1); for (int j = start; j <= 27 end - 1; j++) { if current element is smaller than the pivot (a[j] < pivot) i++; increment index of int t="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="t;" } a[i+1]="a[end];" a[end]="t;" return (i + 1); * function to implement quick sort void quick(int a[], start, end) a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, (start p="partition(a," end); partitioning quick(a, 1, print an array printarr(int n) i; for i n; i++) printf('%d ', a[i]); main() 24, 9, 29, 14, 19, }; n="sizeof(a)" sizeof(a[0]); printf('before sorting elements are
'); printarr(a, n); 0, printf('
after 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-14.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quick sort in C++ language.</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ int partition (int a[], int start, int end) { int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element int i = (start - 1); for (int j = start; j <= 26 end - 1; j++) { if current element is smaller than the pivot (a[j] < pivot) i++; increment index of int t="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="t;" } a[i+1]="a[end];" a[end]="t;" return (i + 1); * function to implement quick sort void quick(int a[], start, end) a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, (start p="partition(a," end); partitioning quick(a, 1, print an array printarr(int n) i; for i n; i++) cout< <a[i]<< ' '; main() 23, 8, 28, 13, 18, }; n="sizeof(a)" sizeof(a[0]); cout<<'before sorting elements are
'; printarr(a, n); 0, cout<<'
after 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-15.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quicksort in python.</p> <pre> #function that consider last element as pivot, #place the pivot at its exact position, and place #smaller elements to left of pivot and greater #elements to right of pivot. def partition (a, start, end): i = (start - 1) pivot = a[end] # pivot element for j in range(start, end): # If current element is smaller than or equal to the pivot if (a[j] <= 1 pivot): i="i" + a[i], a[j]="a[j]," a[i] a[i+1], a[end]="a[end]," a[i+1] return (i 1) # function to implement quick sort def quick(a, start, end): a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, end="Ending" index if (start < p="partition(a," end) is partitioning - 1, printarr(a): print the array for in range(len(a)): (a[i], ) a="[68," 13, 49, 58] print('before sorting elements are ') printarr(a) 0, len(a)-1) print('
after pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-16.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quicksort in Java.</p> <pre> public class Quick { /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ int partition (int a[], int start, int end) { int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element int i = (start - 1); for (int j = start; j <= 25 end - 1; j++) { if current element is smaller than the pivot (a[j] < pivot) i++; increment index of int t="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="t;" } a[i+1]="a[end];" a[end]="t;" return (i + 1); * function to implement quick sort void quick(int a[], start, end) a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, (start p="partition(a," end); partitioning quick(a, 1, print an array printarr(int n) i; for i n; i++) system.out.print(a[i] ' '); public static main(string[] args) 13, 18, 27, 2, 19, }; n="a.length;" system.out.println('
before sorting elements are q1="new" quick(); q1.printarr(a, n); q1.quick(a, 0, system.out.println('
after system.out.println(); pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <p>After the execution of above code, the output will be -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-17.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quick sort in php.</p> <pre> <?php /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ function partition (&$a, $start, $end) { $pivot = $a[$end]; // pivot element $i = ($start - 1); for ($j = $start; $j <= $end - 1; $j++) { // If current element is smaller than the pivot if ($a[$j] < $pivot) { $i++; // increment index of smaller element $t = $a[$i]; $a[$i] = $a[$j]; $a[$j] = $t; } } $t = $a[$i+1]; $a[$i+1] = $a[$end]; $a[$end] = $t; return ($i + 1); } /* function to implement quick sort */ function quick(&$a, $start, $end) /* a[] = array to be sorted, start = Starting index, end = Ending index */ { if ($start < $end) { $p = partition($a, $start, $end); //p is partitioning index quick($a, $start, $p - 1); quick($a, $p + 1, $end); } } function printArray($a, $n) { for($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) { print_r($a[$i]); echo ' '; } } $a = array( 89, 47, 2, 17, 8, 19 ); $n = count($a); echo 'Before sorting array elements are - <br>'; printArray($a, $n); quick($a, 0, $n - 1); echo ' <br> After sorting array elements are - <br>'; printArray($a, $n); ?> </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <p>After the execution of above code, the output will be -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-18.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>So, that's all about the article. Hope the article will be helpful and informative to you.</p> <p>This article was not only limited to the algorithm. Along with the algorithm, we have also discussed the quick sort complexity, working, and implementation in different programming languages.</p> <hr></=></pre></=></pre></=></pre></=></pre></a[right],></p></a[left],></p></a[right],></p></pivot)></pre></end)> Ieșire
După executarea codului de mai sus, rezultatul va fi -

Deci, asta e totul despre articol. Sper că articolul vă va fi util și informativ.
Acest articol nu sa limitat doar la algoritm. Împreună cu algoritmul, am discutat și despre complexitatea sortării rapide, funcționarea și implementarea în diferite limbaje de programare.
tutorial ssis
