În Java, Heap este un tip special de structură de date în care nodul rădăcină sau nodul părinte este comparat cu copiii săi din stânga și din dreapta și aranjat în funcție de ordine. Să presupunem că x este un nod rădăcină și y este nodul copil, proprietate cheie(x)<= key(y)< strong>va genera min-heap și acea relație este denumită „Proprietate Heap” .
Pe baza ordinii nodurilor părinte și copil, Heap poate fi clasificat în două forme, adică Heap min și Heap maxim. Să le înțelegem pe amândouă unul câte unul și să implementăm codul în Java.
cartografiere dactilografiată
Min grămadă
Heap min este un tip special de structură de date heap care este un arbore binar complet în sine. Heap-ul min are următoarele proprietăți:
- Valoarea nodului rădăcină este întotdeauna mai mică în comparație cu celelalte noduri ale heap-ului.
- Fiecare nod intern are o valoare cheie care este întotdeauna mai mică sau egală cu copiii săi.
Putem efectua următoarele trei operații în heap min:
insertNode()
Putem efectua inserarea în heap-ul Min adăugând o nouă cheie la sfârșitul arborelui. Dacă valoarea cheii introduse este mai mică decât nodul părinte, trebuie să traversăm cheia în sus pentru a îndeplini proprietatea heap. Procesul de inserare durează O(log n) timp.
extractMin()
Este una dintre cele mai importante operații pe care le efectuăm pentru a elimina nodul cu valoare minimă, adică nodul rădăcină al heap-ului. După eliminarea nodului rădăcină, trebuie să ne asigurăm că proprietatea heap trebuie menținută. Operația extractMin() necesită timp O(Logn) pentru a elimina elementul minim din heap.
algoritmul k-nn
getMin()
The getMin() operația este utilizată pentru a obține nodul rădăcină al heap-ului, adică elementul minim în timpul O(1).
Exemplu:
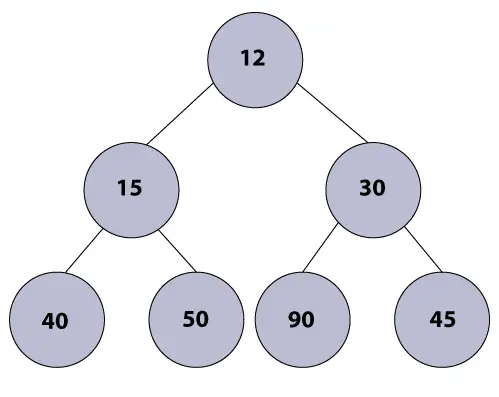
Algoritmul min heap
proceduredesign_min_heap Array arr: of size n => array of elements // call min_heapify procedure for each element of the array to form min heap repeat for (k = n/2 ; k >= 1 ; k--) call procedure min_heapify (arr, k); proceduremin_heapify (vararr[ ] , var k, varn) { varleft_child = 2*k; varright_child = 2*k+1; var smallest; if(left_child<= n and arr[left_child ] <arr[ k ) smallest="left_child;" else if(right_child<="n" arr[right_child <arr[smallest] if(smallest !="k)" { swaparr[ arr[ ]); callmin_heapify (arr, smallest, n); } < pre> <p> <strong>MinHeapJavaImplementation.java</strong> </p> <pre> // import required classes and packages packagejavaTpoint.javacodes; importjava.util.Scanner; // create class MinHeap to construct Min heap in Java classMinHeap { // declare array and variables privateint[] heapData; privateintsizeOfHeap; privateintheapMaxSize; private static final int FRONT = 1; //use constructor to initialize heapData array publicMinHeap(intheapMaxSize) { this.heapMaxSize = heapMaxSize; this.sizeOfHeap = 0; heapData = new int[this.heapMaxSize + 1]; heapData[0] = Integer.MIN_VALUE; } // create getParentPos() method that returns parent position for the node privateintgetParentPosition(int position) { return position / 2; } // create getLeftChildPosition() method that returns the position of left child privateintgetLeftChildPosition(int position) { return (2 * position); } // create getRightChildPosition() method that returns the position of right child privateintgetRightChildPosition(int position) { return (2 * position) + 1; } // checks whether the given node is leaf or not privatebooleancheckLeaf(int position) { if (position >= (sizeOfHeap / 2) && position heapData[getLeftChildPosition(position)] || heapData[position] >heapData[getRightChildPosition(position)]) { // swap with left child and then heapify the left child if (heapData[getLeftChildPosition(position)] = heapMaxSize) { return; } heapData[++sizeOfHeap] = data; int current = sizeOfHeap; while (heapData[current] <heapdata[getparentposition(current)]) { swap(current, getparentposition(current)); current="getParentPosition(current);" } crreatedisplayheap() method to print the data of heap public void displayheap() system.out.println('parent node' + ' ' 'left child 'right node'); for (int k="1;" position--) minheapify(position); create removeroot() removing minimum element from publicintremoveroot() intpopelement="heapData[FRONT];" heapdata[front]="heapData[sizeOfHeap--];" minheapify(front); returnpopelement; minheapjavaimplementation class in java classminheapjavaimplementation{ main() start static main(string[] arg) declare variable intheapsize; scanner object sc="new" scanner(system.in); system.out.println('enter size min heap'); heapsize="sc.nextInt();" minheapheapobj="new" minheap(heapsize); for(inti="1;" i<="heapSize;" i++) system.out.print('enter '+i+' element: '); int heapobj.insertnode(data); close obj sc.close(); construct a given heapobj.designminheap(); display system.out.println('the is heapobj.displayheap(); root node system.out.println('after element(root node) '+heapobj.removeroot()+', is:'); < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/97/heap-implementation-java-2.webp" alt="Heap implementation in Java"> <h2>Max heap</h2> <p>Max heap is another special type of heap data structure that is also a complete binary tree in itself in Java. Max heap has the following properties:</p> <ol class="points"> <li>Root node value is always greater in comparison to the other nodes of the heap.</li> <li>Each internal node has a key value that is always greater or equal to its children.</li> </ol> <p>We can perform the following three operations in Max heap:</p> <h3>insertNode()</h3> <p>We can perform insertion in the Max heap by adding a new key at the end of the tree. If the value of the inserted key is greater than its parent node, we have to traverse the key upwards for fulfilling the heap property. The insertion process takes O(log n) time.</p> <h3>extractMax()</h3> <p>It is one of the most important operations which we perform to remove the maximum value node, i.e., the root node of the heap. After removing the root node, we have to make sure that heap property should be maintained. The extractMax() operation takes O(Log n) time to remove the maximum element from the heap.</p> <h3>getMax()</h3> <p>The <strong>getMax()</strong> operation is used to get the root node of the heap, i.e., maximum element in O(1) time.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/97/heap-implementation-java-3.webp" alt="Heap implementation in Java"> <p> <strong>Min heap Algorithm</strong> </p> <pre> proceduredesign_max_heap Array arr: of size n => array of elements // call min_heapify procedure for each element of the array to form max heap repeat for (k = n/2 ; k >= 1 ; k--) call procedure max_heapify (arr, k); proceduremin_heapify (vararr[ ] , var k, varn) { varleft_child = 2*k + 1; varright_child = 2*k+ 2; if(left_childarr[ largest ] ) largest = left_child; else largest = k; if(right_childarr[largest] ) largest = right_child; if(largest != k) { swaparr[ k ] and arr[ largest ]); callmax_heapify (arr, largest, n); } } </pre> <p> <strong>MaxHeapJavaImplementation.java</strong> </p> <pre> //import required classes and packages packagejavaTpoint.javacodes; importjava.util.Scanner; //create class MinHeap to construct Min heap in Java classMaxHeap { // declare array and variables privateint[] heapData; privateintsizeOfHeap; privateintheapMaxSize; private static final int FRONT = 1; //use constructor to initialize heapData array publicMaxHeap(intheapMaxSize) { this.heapMaxSize = heapMaxSize; this.sizeOfHeap = 0; heapData = new int[this.heapMaxSize]; } // create getParentPos() method that returns parent position for the node privateintgetParentPosition(int position) { return (position - 1) / 2; } // create getLeftChildPosition() method that returns the position of left child privateintgetLeftChildPosition(int position) { return (2 * position); } // create getRightChildPosition() method that returns the position of right child privateintgetRightChildPosition(int position) { return (2 * position) + 1; } // checks whether the given node is leaf or not privatebooleancheckLeaf(int position) { if (position > (sizeOfHeap / 2) && position <= sizeofheap) { return true; } false; create swapnodes() method that perform swapping of the given nodes heap firstnode and secondnode are positions private void swap(intfirstnode, intsecondnode) int temp; temp="heapData[firstNode];" heapdata[firstnode]="heapData[secondNode];" heapdata[secondnode]="temp;" maxheapify() to heapify node for maintaining property maxheapify(int position) check whether is non-leaf greater than its right left child if (!checkleaf(position)) (heapdata[position] <heapdata[getleftchildposition(position)] || heapdata[position] heapdata[getrightchildposition(position)]) swap(position, getleftchildposition(position)); maxheapify(getleftchildposition(position)); swap with else getrightchildposition(position)); maxheapify(getrightchildposition(position)); insertnode() insert element in public insertnode(int data) heapdata[sizeofheap]="data;" current="sizeOfHeap;" while (heapdata[current]>heapData[getParentPosition(current)]) { swap(current, getParentPosition(current)); current = getParentPosition(current); } sizeOfHeap++; } // create displayHeap() method to print the data of the heap public void displayHeap() { System.out.println('PARENT NODE' + ' ' + 'LEFT CHILD NODE' + ' ' + 'RIGHT CHILD NODE'); for (int k = 0; k <sizeofheap 2; k++) { system.out.print(' ' + heapdata[k] ' ' heapdata[2 * k 1] 2]); system.out.println(); } create designmaxheap() method to construct min heap public void for (int position="0;" < (sizeofheap 2); position++) maxheapify(position); removeroot() removing maximum element from the publicintremoveroot() intpopelement="heapData[FRONT];" heapdata[front]="heapData[sizeOfHeap--];" maxheapify(front); returnpopelement; minheapjavaimplementation class in java classmaxheapjavaimplementation{ main() start static main(string[] arg) declare variable intheapsize; scanner object sc="new" scanner(system.in); system.out.println('enter size of max heap'); heapsize="sc.nextInt();" maxheapheapobj="new" maxheap(50); for(inti="1;" i<="heapSize;" i++) system.out.print('enter '+i+' element: '); int data="sc.nextInt();" heapobj.insertnode(data); close obj sc.close(); a given heapobj.designmaxheap(); display system.out.println('the is heapobj.displayheap(); root node system.out.println('after element(root node) '+heapobj.removeroot()+', is:'); pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/97/heap-implementation-java-4.webp" alt="Heap implementation in Java"> <hr></sizeofheap></=></pre></heapdata[getparentposition(current)])></pre></=> MaxHeapJavaImplementation.java
//import required classes and packages packagejavaTpoint.javacodes; importjava.util.Scanner; //create class MinHeap to construct Min heap in Java classMaxHeap { // declare array and variables privateint[] heapData; privateintsizeOfHeap; privateintheapMaxSize; private static final int FRONT = 1; //use constructor to initialize heapData array publicMaxHeap(intheapMaxSize) { this.heapMaxSize = heapMaxSize; this.sizeOfHeap = 0; heapData = new int[this.heapMaxSize]; } // create getParentPos() method that returns parent position for the node privateintgetParentPosition(int position) { return (position - 1) / 2; } // create getLeftChildPosition() method that returns the position of left child privateintgetLeftChildPosition(int position) { return (2 * position); } // create getRightChildPosition() method that returns the position of right child privateintgetRightChildPosition(int position) { return (2 * position) + 1; } // checks whether the given node is leaf or not privatebooleancheckLeaf(int position) { if (position > (sizeOfHeap / 2) && position <= sizeofheap) { return true; } false; create swapnodes() method that perform swapping of the given nodes heap firstnode and secondnode are positions private void swap(intfirstnode, intsecondnode) int temp; temp="heapData[firstNode];" heapdata[firstnode]="heapData[secondNode];" heapdata[secondnode]="temp;" maxheapify() to heapify node for maintaining property maxheapify(int position) check whether is non-leaf greater than its right left child if (!checkleaf(position)) (heapdata[position] <heapdata[getleftchildposition(position)] || heapdata[position] heapdata[getrightchildposition(position)]) swap(position, getleftchildposition(position)); maxheapify(getleftchildposition(position)); swap with else getrightchildposition(position)); maxheapify(getrightchildposition(position)); insertnode() insert element in public insertnode(int data) heapdata[sizeofheap]="data;" current="sizeOfHeap;" while (heapdata[current]>heapData[getParentPosition(current)]) { swap(current, getParentPosition(current)); current = getParentPosition(current); } sizeOfHeap++; } // create displayHeap() method to print the data of the heap public void displayHeap() { System.out.println('PARENT NODE' + ' ' + 'LEFT CHILD NODE' + ' ' + 'RIGHT CHILD NODE'); for (int k = 0; k <sizeofheap 2; k++) { system.out.print(\' \' + heapdata[k] \' \' heapdata[2 * k 1] 2]); system.out.println(); } create designmaxheap() method to construct min heap public void for (int position="0;" < (sizeofheap 2); position++) maxheapify(position); removeroot() removing maximum element from the publicintremoveroot() intpopelement="heapData[FRONT];" heapdata[front]="heapData[sizeOfHeap--];" maxheapify(front); returnpopelement; minheapjavaimplementation class in java classmaxheapjavaimplementation{ main() start static main(string[] arg) declare variable intheapsize; scanner object sc="new" scanner(system.in); system.out.println(\'enter size of max heap\'); heapsize="sc.nextInt();" maxheapheapobj="new" maxheap(50); for(inti="1;" i<="heapSize;" i++) system.out.print(\'enter \'+i+\' element: \'); int data="sc.nextInt();" heapobj.insertnode(data); close obj sc.close(); a given heapobj.designmaxheap(); display system.out.println(\'the is heapobj.displayheap(); root node system.out.println(\'after element(root node) \'+heapobj.removeroot()+\', is:\'); pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/97/heap-implementation-java-4.webp" alt="Heap implementation in Java"> <hr></sizeofheap></=>