Buclele în limbajul C sunt instrucțiunile fluxului de control care sunt folosite pentru a repeta o parte a codului până când condiția dată este îndeplinită. The bucla do-while este una dintre cele trei instrucțiuni de buclă din C, celelalte fiind buclă while și buclă for. Este folosit în principal pentru a traversa matrice, vectori și alte structuri de date.
Ce este do...while Loop în C?
The face... în timp ce în C este o instrucțiune în buclă folosită pentru a repeta o parte a codului până când condiția dată este îndeplinită. Este o formă de an buclă controlată de ieșire sau post-testată unde se verifică condiția de testare după executarea corpului buclei. Din acest motiv, instrucțiunile din bucla do...while vor fi întotdeauna executate cel puțin o dată, indiferent de condiția.
Sintaxa lui do…while Loop în C
do { // body of do-while loop } while ( condition );> Cum se utilizează do...while Loop în C
Următorul exemplu demonstrează utilizarea buclei do...while în limbajul de programare C.
C
// C Program to demonstrate the use of do...while loop> #include> int> main()> {> >// loop variable declaration and initialization> >int> i = 0;> >// do while loop> >do> {> >printf>(>'Geeks
'>);> >i++;> >}>while> (i <3);> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>Ieșire
Geeks Geeks Geeks>
Cum funcționează... în timp ce Loop funcționează?

Sintaxă Structura buclei do while
Funcționarea buclei do…while este explicată mai jos:
- Când controlul programului ajunge pentru prima dată la bucla do...while, se execută mai întâi corpul buclei și apoi se verifică condiția/expresia de testare , spre deosebire de alte bucle în care condiția de testare este verificată mai întâi. Datorită acestei proprietăți, bucla do…while se mai numește și buclă controlată de ieșire sau post-testată.
- Când starea de testare este evaluată ca Adevărat , cel controlul programului merge la început a buclei și corpul se execută încă o dată.
- Procesul de mai sus se repetă până când condiția de testare este adevărată.
- Când starea de testare este evaluată ca fals, controalele programului trec la următoarele instrucțiuni după bucla do…while.
Ca și în cazul buclei while din C, inițializarea și actualizarea nu fac parte din sintaxa buclei do...while. Trebuie să facem asta în mod explicit înainte și, respectiv, în buclă.
Diagrama de mai jos arată reprezentarea vizuală a fluxului buclei do...while în C.
C do...while Loop Flowchart
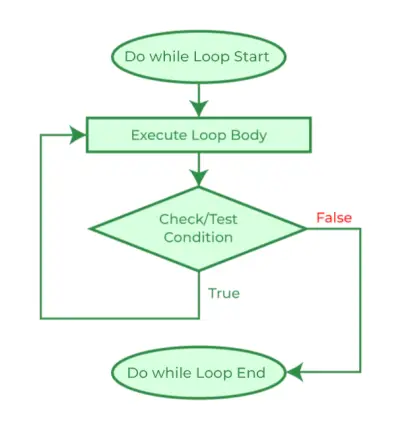
Organigrama do…while Loop în C
Imbricat do...while Loop în C
Ca și în cazul celorlalte bucle, putem, de asemenea, să imbricați o buclă do...while în bucla într-o altă buclă. Este demonstrat folosind următorul program C.
Exemplu de Imbricat do...while Loop în C:
C
// C Program to demonstrate the nesting of do...while loop> #include> int> main()> {> >// declaring loop variables> >int> i = 0, j;> >int> count = 0;> >// outer loop starts> >do> {> >j = 0;> >// inner loop starts> >do> {> >printf>(>'%d '>, count++);> >j++;> >}>while> (j <3);> >// inner loop ends> >printf>(>'
'>);> >i++;> >}>while> (i <3);> >// outer loop ends> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>Ieșire
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8>
Pentru a afla mai multe despre bucle imbricate în C, consultați acest articol - Bucle imbricate în C cu exemple
Exemple de do...while Loop în C
Exemplul 1. C Program pentru a demonstra comportamentul buclei do…while dacă condiția este falsă de la început.
C
regex java
// C Program to demonstrate the do...while loop behaviour> // when the condition is false from the start> #include> #include> int> main()> {> >// declaring a false variable> >bool> condition =>false>;> >do> {> >printf>(>'This is loop body.'>);> >}>while> (condition);>// false condition> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>Ieșire
This is loop body.>
După cum putem vedea, chiar și atunci când condiția este falsă la început, corpul buclei este executat o dată. Acest lucru se datorează faptului că în bucla do...while, starea este verificată după ce a trecut prin corp, așa că atunci când controlul este la început,
- Trece prin corpul buclei.
- Execută toate declarațiile din corp.
- Verifică condiția care se dovedește a fi falsă.
- Apoi iese din buclă.
Exemplul 2. C Program pentru a tipări Tabelul de înmulțire a lui N folosind bucla do…while
Următorul exemplu demonstrează utilizarea buclei do...while pentru tipărirea tabelului de înmulțire a lui N.
C
// C Program to print multiplication table using do...while> // loop> #include> int> main()> {> >int> N = 5, i = 1;> >do> {> >printf>(>'%d x %d = %d
'>, N, i, N * i);> >}>while> (i++ <10);> >return> 0;> }> |
>
exemple de automate dfa
>Ieșire
5 x 1 = 5 5 x 2 = 10 5 x 3 = 15 5 x 4 = 20 5 x 5 = 25 5 x 6 = 30 5 x 7 = 35 5 x 8 = 40 5 x 9 = 45 5 x 10 = 50>
Diferența dintre while și do...while Loop în C
Următorul tabel listează cele mai importante diferențele dintre while și do...while Loop în C.
| în timp ce Loop | face... în timp ce Loop |
|---|---|
| Se verifică starea de testare înainte ca corpul buclei să fie executat. | Se verifică starea de testare după executarea corpului. |
| Când condiția este falsă, corpul nu este executat nici macar o data. | Corpul lui do...while bucla este executată cel puțin o dată chiar și atunci când condiția este falsă. |
| Este un tip de buclă pre-testată sau controlată de intrare. | Este un tip de buclă post-testată sau controlată de ieșire. |
| Nu este necesar punctul și virgulă. | Punctul și virgulă este necesar la sfârșit. |
Pentru a afla mai multe despre aceste diferențe, consultați acest articol - Diferența dintre bucla while și do-while în C, C++, Java
Concluzie
În concluzie, utilizarea singurei bucle controlate de ieșire din C, bucla do...while este, de asemenea, pentru a repeta o anumită parte a codului, dar modul în care funcționează o face diferită de buclele controlate de intrare, cum ar fi bucla while și for buclă. Este util în cazurile în care trebuie să executăm instrucțiunea în corpul buclei cel puțin o dată, cum ar fi parcurgerea listelor circulare legate.
Întrebări frecvente despre C do...while Loops
1. Câte tipuri de bucle există în C?
Ani: Există 3 tipuri de bucle în limbajul C:
- pentru Loop
- în timp ce Loop
- face... în timp ce Loop
2. Care sunt buclele controlate de intrare sau pre-testate?
Ani: Buclele controlate de intrare sau buclele pre-testate sunt acele bucle în care bucla starea este verificată înainte de a executa corpul a buclei.
3. Care sunt buclele controlate de ieșire sau post-testate?
Ani: Buclele controlate de ieșire sau buclele post-testate sunt acele bucle în care controlul programului ajunge la corpul buclei înainte de a verifica starea buclei .
4. Care buclă este garantată să se execute cel puțin o dată?
Ani: The face... în timp ce buclă este garantat să execute instrucțiunile din corpul buclei cel puțin o dată, deoarece este un tip de buclă controlată de ieșire.
5. Putem sări peste acolade în C do...while sintaxa buclei dacă există o singură declarație în corp?
Răspuns: Nu. , nu putem sări peste acolade în sintaxa C do...while chiar dacă există doar o singură instrucțiune, spre deosebire de bucla while și for.
6. Cum se creează o buclă infinită în C folosind bucla do...while?
Ani: Putem crea o buclă infinită în C specificând a condiție care va fi întotdeauna adevărată ca condiție de buclă. Programul de mai jos demonstrează cum să faci asta:
C
// C Program to create a infinite loop using do...while loop> // in C> #include> int> main()> {> >// infinite loop> >do> {> >printf>(>'gfg '>);> >}>while> (1);>// always 1 ~ true> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Ieșire
gfg gfg gfg gfg gfg gfg gfg .... (infinite)>
