Având în vedere un set gol inițial și o serie de întrebări pe acesta, fiecare dintre următoarele tipuri:
- Inserarea „X” se face folosind actualizarea (1 0 10^6 x 1). Rețineți că rădăcina arborelui este transmisă indicele de pornire este trecut ca 0 și indicele de sfârșit ca 10^6, astfel încât toate intervalele care au x sunt actualizate.
- Ștergerea „X” se face folosind actualizarea (1 0 10^6 x -1). Rețineți că rădăcina arborelui este transmisă indicele de pornire este trecut ca 0 și indicele de sfârșit ca 10^6, astfel încât toate intervalele care au x sunt actualizate.
Exemplu:
Input : Insert 1 Insert 4 Insert 7 Median Output : The first three queries should insert 1 4 and 7 into an empty set. The fourth query should return 4 (median of 1 4 7).
În scop de expunere, presupunem următoarele, dar aceste presupuneri nu sunt limitările metodei discutate aici:
1. În orice caz, toate elementele sunt distincte care nu este niciunul dintre ele să nu aibă loc de mai multe ori.
2. Interogarea „mediană” se face numai atunci când există un număr ciudat de elemente în set. (Va trebui să facem două întrebări pe arborele nostru de segment în caz de numere chiar)
3. Elementele din set variază de la 1 la +10^6.
Metoda 1 (naivă)
În implementarea naivă, putem face primele două întrebări în O (1), dar ultima interogare în O (MAX_ELEM) unde max_elem este elementul maxim din toate timpurile (inclusiv elemente șterse).
Să ne asumăm un tablou conta[] (de dimensiunea 10^6 + 1) pentru a menține numărul fiecărui element în subset. Următoarele sunt algoritmi simpli și explicativi pentru cei 3 întrebări:
Introduceți x interogare:
count[x]++; if (x > max_elem) max_elem = x; n++;
Ștergeți X interogare:
if (count[x] > 0) count[x]--; n--;
Interogare mediană:
sum = 0; i = 0; while( sum <= n / 2 ) { i++; sum += count[i]; } median = i; return median; Ilustrația numărului de matrice [] reprezentând setul {1 4 7 8 9} Elementul median este „7”:
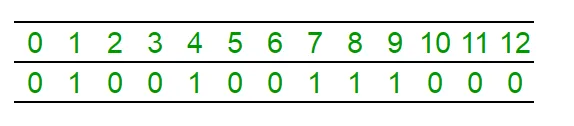
Interogarea „mediană” intenționează să găsească (n + 1)/2 „1” în tablou, în acest caz, al treilea „1”; Acum facem același lucru folosind un arbore de segment.
Metoda 2 (folosind Arbore de segment )
Facem un arbore de segment Pentru a stoca suma de intervale în care un interval [A B] reprezintă numărul de elemente prezente în setul în prezent în intervalul [A B]. De exemplu, dacă luăm în considerare exemplul de mai sus interogarea (3 7) returnează 2 interogare (4 4) returnează 1 interogare (5 5) returnează 0.
Introducerea și ștergerea interogărilor sunt simple și ambele pot fi implementate folosind actualizarea funcțiilor (int x int dif) (adaugă „dif” la indexul „x”)
Algoritm
// adds ‘diff’ at index ‘x’ update(node a b x diff) // If leaf node If a == b and a == x segmentTree[node] += diff // If non-leaf node and x lies in its range If x is in [a b] // Update children recursively update(2*node a (a + b)/2 x diff) update(2*node + 1 (a + b)/2 + 1 b x diff) // Update node segmentTree[node] = segmentTree[2 * node] + segmentTree[2 * node + 1]
Funcția recursivă de mai sus rulează O (jurnal (max_elem)) (În acest caz, max_elem este 10^6) și utilizat atât pentru inserție, cât și pentru ștergere cu următoarele apeluri:
Acum, funcția de a găsi indexul cu Kth „1” în care „K” în acest caz va fi întotdeauna (n + 1) / 2, aceasta va funcționa foarte mult ca căutarea binară, puteți gândi la el ca o funcție de căutare binară recursivă pe un arbore de segment.
Să luăm un exemplu pentru a înțelege că setul nostru are în prezent elemente {1 4 7 8 9} și, prin urmare, este reprezentat de următorul arbore de segment.
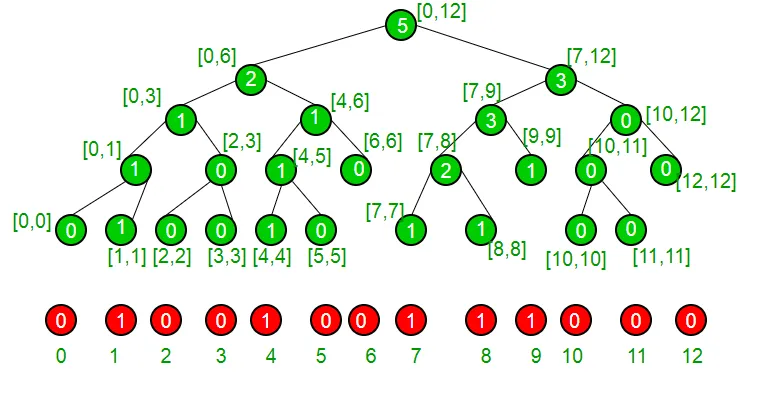
Dacă suntem la un nod non-frunze, suntem siguri că are ambii copii, vedem dacă copilul din stânga are un număr mai mare sau egal de „k”, dacă da, suntem siguri că indicele nostru se află în subtree stânga, altfel, dacă subtree stânga are un număr mai mic de 1 decât K, atunci suntem siguri că indexul nostru se află în subtree dreapta. Facem acest lucru recursiv pentru a ajunge la indexul nostru și de acolo îl returnăm.
Algoritm
1.findKth(node a b k) 2. If a != b 3. If segmentTree[ 2 * node ] >= k 4. return findKth(2*node a (a + b)/2 k) 5. else 6. return findKth(2*node + 1 (a + b)/2 + 1 b k - segmentTree[ 2 * node ]) 7. else 8. return a
Funcția recursivă de mai sus rulează O (jurnal (max_elem)) .
// A C++ program to implement insert delete and // median queries using segment tree #include
// A Java program to implement insert delete and // median queries using segment tree import java.io.*; class GFG{ public static int maxn = 3000005; public static int max_elem = 1000000; // A global array to store segment tree. // Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. public static int[] segmentTree = new int[maxn]; // Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. // Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and // 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored // in current node. // 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. public static void update(int node int a int b int x int diff) { // If current node is a leaf node if (a == b && a == x ) { // Add 'diff' and return segmentTree[node] += diff; return ; } // If current node is non-leaf and 'x' // is in its range if (x >= a && x <= b) { // Update both sub-trees left and right update(node * 2 a (a + b) / 2 x diff); update(node * 2 + 1 (a + b) / 2 + 1 b x diff); // Finally update current node segmentTree[node] = segmentTree[node * 2] + segmentTree[node * 2 + 1]; } } // Returns k'th node in segment tree public static int findKth(int node int a int b int k) { // Non-leaf node will definitely have both // children; left and right if (a != b) { // If kth element lies in the left subtree if (segmentTree[node * 2] >= k) { return findKth(node * 2 a (a + b) / 2 k); } // If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth(node * 2 + 1 (a + b) / 2 + 1 b k - segmentTree[node * 2]); } // If at a leaf node return the index it stores // information about return (segmentTree[node] != 0) ? a : -1; } // Insert x in the set public static void insert(int x) { update(1 0 max_elem x 1); } // Delete x from the set public static void delete(int x) { update(1 0 max_elem x -1); } // Returns median element of the set // with odd cardinality only public static int median() { int k = (segmentTree[1] + 1) / 2; return findKth(1 0 max_elem k); } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { insert(1); insert(4); insert(7); System.out.println('Median for the set {147} = ' + median()); insert(8); insert(9); System.out.println('Median for the set {14789} = ' + median()); delete(1); delete(8); System.out.println('Median for the set {479} = ' + median()); } } // This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
# A Python3 program to implement insert delete and # median queries using segment tree maxn = 3000005 max_elem = 1000000 # A global array to store segment tree. # Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. segmentTree = [0 for i in range(maxn)] # Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. # Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and # 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored # in current node. # 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. def update(node a b x diff): global segmentTree # If current node is a leaf node if (a == b and a == x ): # add 'diff' and return segmentTree[node] += diff return # If current node is non-leaf and 'x' is in its # range if (x >= a and x <= b): # update both sub-trees left and right update(node * 2 a (a + b)//2 x diff) update(node * 2 + 1 (a + b)//2 + 1 b x diff) # Finally update current node segmentTree[node] = segmentTree[node * 2] + segmentTree[node * 2 + 1] # Returns k'th node in segment tree def findKth(node a b k): global segmentTree # non-leaf node will definitely have both # children left and right if (a != b): # If kth element lies in the left subtree if (segmentTree[node * 2] >= k): return findKth(node * 2 a (a + b)//2 k) # If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth(node * 2 + 1 (a + b)//2 + 1 b k - segmentTree[node * 2]) # if at a leaf node return the index it stores # information about return a if (segmentTree[node]) else -1 # insert x in the set def insert(x): update(1 0 max_elem x 1) # delete x from the set def delete(x): update(1 0 max_elem x -1) # returns median element of the set with odd # cardinality only def median(): k = (segmentTree[1] + 1) // 2 return findKth(1 0 max_elem k) # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': insert(1) insert(4) insert(7) print('Median for the set {147} ='median()) insert(8) insert(9) print('Median for the set {14789} ='median()) delete(1) delete(8) print('Median for the set {479} ='median()) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
// A C# program to implement insert delete // and median queries using segment tree using System; class GFG{ public static int maxn = 3000005; public static int max_elem = 1000000; // A global array to store segment tree. // Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. public static int[] segmentTree = new int[maxn]; // Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. // Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and // 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored // in current node. // 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. public static void update(int node int a int b int x int diff) { // If current node is a leaf node if (a == b && a == x) { // Add 'diff' and return segmentTree[node] += diff; return ; } // If current node is non-leaf and 'x' // is in its range if (x >= a && x <= b) { // Update both sub-trees left and right update(node * 2 a (a + b) / 2 x diff); update(node * 2 + 1 (a + b) / 2 + 1 b x diff); // Finally update current node segmentTree[node] = segmentTree[node * 2] + segmentTree[node * 2 + 1]; } } // Returns k'th node in segment tree public static int findKth(int node int a int b int k) { // Non-leaf node will definitely have both // children; left and right if (a != b) { // If kth element lies in the left subtree if (segmentTree[node * 2] >= k) { return findKth(node * 2 a (a + b) / 2 k); } // If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth(node * 2 + 1 (a + b) / 2 + 1 b k - segmentTree[node * 2]); } // If at a leaf node return the index it // stores information about if (segmentTree[node] != 0) { return a; } else { return -1; } } // Insert x in the set public static void insert(int x) { update(1 0 max_elem x 1); } // Delete x from the set public static void delete(int x) { update(1 0 max_elem x -1); } // Returns median element of the set // with odd cardinality only public static int median() { int k = (segmentTree[1] + 1) / 2; return findKth(1 0 max_elem k); } // Driver code static public void Main() { insert(1); insert(4); insert(7); Console.WriteLine('Median for the set {147} = ' + median()); insert(8); insert(9); Console.WriteLine('Median for the set {14789} = ' + median()); delete(1); delete(8); Console.WriteLine('Median for the set {479} = ' + median()); } } // This code is contributed by rag2127
<script> // A Javascript program to implement insert delete and // median queries using segment tree let maxn = 3000005; let max_elem = 1000000; // A global array to store segment tree. // Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. let segmentTree = new Array(maxn); for(let i=0;i<maxn;i++) { segmentTree[i]=0; } // Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. // Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and // 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored // in current node. // 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. function update(nodeabxdiff) { // If current node is a leaf node if (a == b && a == x ) { // Add 'diff' and return segmentTree[node] += diff; return ; } // If current node is non-leaf and 'x' // is in its range if (x >= a && x <= b) { // Update both sub-trees left and right update(node * 2 a Math.floor((a + b) / 2) x diff); update(node * 2 + 1 Math.floor((a + b) / 2) + 1 b x diff); // Finally update current node segmentTree[node] = segmentTree[node * 2] + segmentTree[node * 2 + 1]; } } // Returns k'th node in segment tree function findKth(nodeabk) { // Non-leaf node will definitely have both // children; left and right if (a != b) { // If kth element lies in the left subtree if (segmentTree[node * 2] >= k) { return findKth(node * 2 a Math.floor((a + b) / 2) k); } // If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth(node * 2 + 1 Math.floor((a + b) / 2) + 1 b k - segmentTree[node * 2]); } // If at a leaf node return the index it stores // information about return (segmentTree[node] != 0) ? a : -1; } // Insert x in the set function insert(x) { update(1 0 max_elem x 1); } // Delete x from the set function delet(x) { update(1 0 max_elem x -1); } // Returns median element of the set // with odd cardinality only function median() { let k = (segmentTree[1] + 1) / 2; return findKth(1 0 max_elem k); } // Driver code insert(1); insert(4); insert(7); document.write('Median for the set {147} = ' + median()+'
'); insert(8); insert(9); document.write('Median for the set {14789} = ' + median()+'
'); delet(1); delet(8); document.write('Median for the set {479} = ' + median()+'
'); // This code is contributed by unknown2108 </script>
Ieșire:
Median for the set {147} = 4 Median for the set {14789} = 7 Median for the set {479} = 7
Concluzie:
Toate cele trei întrebări rulează O (jurnal (max_elem)) În acest caz, max_elem = 10^6 so log (max_elem) este aproximativ egal cu 20.
Arborele segmentului folosește O (max_elem) spaţiu.
Dacă interogarea de ștergere nu ar fi fost, problema s -ar fi putut face și cu un algoritm celebru Aici .
