Matricea 2D poate fi definită ca o matrice de matrice. Matricea 2D este organizată ca matrici care pot fi reprezentate ca o colecție de rânduri și coloane.
Cu toate acestea, tablourile 2D sunt create pentru a implementa o structură de date similară cu o bază de date relațională. Oferă ușurință în păstrarea unui volum mare de date simultan, care pot fi transmise la orice număr de funcții oriunde este necesar.
Cum se declară 2D Array
Sintaxa declarării unui tablou bidimensional este foarte asemănătoare cu cea a unui tablou unidimensional, dată după cum urmează.
int arr[max_rows][max_columns];
cu toate acestea, produce structura de date care arată ca următoarea.
webdriver
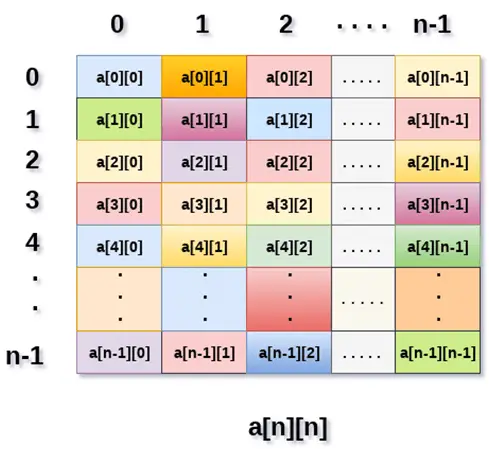
Imaginea de mai sus arată matricea bidimensională, elementele sunt organizate sub formă de rânduri și coloane. Primul element al primului rând este reprezentat de a[0][0] unde numărul afișat în primul index este numărul acelui rând, în timp ce numărul afișat în al doilea index este numărul coloanei.
Cum accesăm datele într-o matrice 2D
Datorită faptului că elementele matricelor 2D pot fi accesate aleatoriu. Similar cu matricele unidimensionale, putem accesa celulele individuale într-o matrice 2D utilizând indicii celulelor. Există doi indici atașați unei anumite celule, unul este numărul rândului său, în timp ce celălalt este numărul coloanei.
iarnă triplă
Cu toate acestea, putem stoca valoarea stocată într-o anumită celulă a unui tablou 2D într-o variabilă x folosind următoarea sintaxă.
int x = a[i][j];
unde i și j sunt numărul rândului și, respectiv, al coloanei celulei.
Putem atribui fiecare celulă a unui tablou 2D la 0 utilizând următorul cod:
for ( int i=0; i<n ;i++) { for (int j="0;" j<n; j++) a[i][j]="0;" } < pre> <h2>Initializing 2D Arrays </h2> <p>We know that, when we declare and initialize one dimensional array in C programming simultaneously, we don't need to specify the size of the array. However this will not work with 2D arrays. We will have to define at least the second dimension of the array. </p> <p>The syntax to declare and initialize the 2D array is given as follows. </p> <pre> int arr[2][2] = {0,1,2,3}; </pre> <p>The number of elements that can be present in a 2D array will always be equal to ( <strong>number of rows * number of columns</strong> ). </p> <p> <strong>Example :</strong> Storing User's data into a 2D array and printing it. </p> <p> <strong>C Example : </strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int arr[3][3],i,j; for (i=0;i<3;i++) { for (j="0;j<3;j++)" printf('enter a[%d][%d]: ',i,j); scanf('%d',&arr[i][j]); } printf('
printing the elements ....
'); for(i="0;i<3;i++)" printf('
'); printf('%d ',arr[i][j]); < pre> <h3>Java Example</h3> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; publicclass TwoDArray { publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) { int[][] arr = newint[3][3]; Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); for (inti =0;i<3;i++) { for(intj="0;j<3;j++)" system.out.print('enter element'); arr[i][j]="sc.nextInt();" system.out.println(); } system.out.println('printing elements...'); for(inti="0;i<3;i++)" system.out.print(arr[i][j]+' '); < pre> <h3>C# Example </h3> <pre> using System; public class Program { public static void Main() { int[,] arr = new int[3,3]; for (int i=0;i<3;i++) { for (int j="0;j<3;j++)" console.writeline('enter element'); arr[i,j]="Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());" } console.writeline('printing elements...'); i="0;i<3;i++)" console.writeline(); console.write(arr[i,j]+' '); < pre> <h2>Mapping 2D array to 1D array </h2> <p>When it comes to map a 2 dimensional array, most of us might think that why this mapping is required. However, 2 D arrays exists from the user point of view. 2D arrays are created to implement a relational database table lookalike data structure, in computer memory, the storage technique for 2D array is similar to that of an one dimensional array. </p> <p>The size of a two dimensional array is equal to the multiplication of number of rows and the number of columns present in the array. We do need to map two dimensional array to the one dimensional array in order to store them in the memory.</p> <p>A 3 X 3 two dimensional array is shown in the following image. However, this array needs to be mapped to a one dimensional array in order to store it into the memory. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-2.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>There are two main techniques of storing 2D array elements into memory </p> <h3>1. Row Major ordering </h3> <p>In row major ordering, all the rows of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. Considering the array shown in the above image, its memory allocation according to row major order is shown as follows. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-3.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last row.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-4.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h3>2. Column Major ordering </h3> <p>According to the column major ordering, all the columns of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. The memory allocation of the array which is shown in in the above image is given as follows.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-5.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> column of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last column of the array. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-6.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h2>Calculating the Address of the random element of a 2D array </h2> <p>Due to the fact that, there are two different techniques of storing the two dimensional array into the memory, there are two different formulas to calculate the address of a random element of the 2D array. </p> <h3>By Row Major Order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = B. A. + (i * n + j) * size </pre> <p>where, B. A. is the base address or the address of the first element of the array a[0][0] . </p> <p> <strong>Example : </strong> </p> <pre> a[10...30, 55...75], base address of the array (BA) = 0, size of an element = 4 bytes . Find the location of a[15][68]. Address(a[15][68]) = 0 + ((15 - 10) x (68 - 55 + 1) + (68 - 55)) x 4 = (5 x 14 + 13) x 4 = 83 x 4 = 332 answer </pre> <h3>By Column major order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = ((j*m)+i)*Size + BA </pre> <p>where BA is the base address of the array. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> A [-5 ... +20][20 ... 70], BA = 1020, Size of element = 8 bytes. Find the location of a[0][30]. Address [A[0][30]) = ((30-20) x 24 + 5) x 8 + 1020 = 245 x 8 + 1020 = 2980 bytes </pre> <hr></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)></pre></n> Numărul de elemente care pot fi prezente într-o matrice 2D va fi întotdeauna egal cu ( numărul de rânduri * numărul de coloane ).
comenzi rapide linux
Exemplu: Stocarea datelor utilizatorului într-o matrice 2D și imprimarea acestora.
C Exemplu:
#include void main () { int arr[3][3],i,j; for (i=0;i<3;i++) { for (j="0;j<3;j++)" printf(\'enter a[%d][%d]: \',i,j); scanf(\'%d\',&arr[i][j]); } printf(\'
printing the elements ....
\'); for(i="0;i<3;i++)" printf(\'
\'); printf(\'%d \',arr[i][j]); < pre> <h3>Java Example</h3> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; publicclass TwoDArray { publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) { int[][] arr = newint[3][3]; Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); for (inti =0;i<3;i++) { for(intj="0;j<3;j++)" system.out.print(\'enter element\'); arr[i][j]="sc.nextInt();" system.out.println(); } system.out.println(\'printing elements...\'); for(inti="0;i<3;i++)" system.out.print(arr[i][j]+\' \'); < pre> <h3>C# Example </h3> <pre> using System; public class Program { public static void Main() { int[,] arr = new int[3,3]; for (int i=0;i<3;i++) { for (int j="0;j<3;j++)" console.writeline(\'enter element\'); arr[i,j]="Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());" } console.writeline(\'printing elements...\'); i="0;i<3;i++)" console.writeline(); console.write(arr[i,j]+\' \'); < pre> <h2>Mapping 2D array to 1D array </h2> <p>When it comes to map a 2 dimensional array, most of us might think that why this mapping is required. However, 2 D arrays exists from the user point of view. 2D arrays are created to implement a relational database table lookalike data structure, in computer memory, the storage technique for 2D array is similar to that of an one dimensional array. </p> <p>The size of a two dimensional array is equal to the multiplication of number of rows and the number of columns present in the array. We do need to map two dimensional array to the one dimensional array in order to store them in the memory.</p> <p>A 3 X 3 two dimensional array is shown in the following image. However, this array needs to be mapped to a one dimensional array in order to store it into the memory. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-2.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>There are two main techniques of storing 2D array elements into memory </p> <h3>1. Row Major ordering </h3> <p>In row major ordering, all the rows of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. Considering the array shown in the above image, its memory allocation according to row major order is shown as follows. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-3.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last row.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-4.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h3>2. Column Major ordering </h3> <p>According to the column major ordering, all the columns of the 2D array are stored into the memory contiguously. The memory allocation of the array which is shown in in the above image is given as follows.</p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-5.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <p>first, the 1<sup>st</sup> column of the array is stored into the memory completely, then the 2<sup>nd</sup> row of the array is stored into the memory completely and so on till the last column of the array. </p> <br> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/80/2d-array-6.webp" alt="DS 2D Array"> <br> <h2>Calculating the Address of the random element of a 2D array </h2> <p>Due to the fact that, there are two different techniques of storing the two dimensional array into the memory, there are two different formulas to calculate the address of a random element of the 2D array. </p> <h3>By Row Major Order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = B. A. + (i * n + j) * size </pre> <p>where, B. A. is the base address or the address of the first element of the array a[0][0] . </p> <p> <strong>Example : </strong> </p> <pre> a[10...30, 55...75], base address of the array (BA) = 0, size of an element = 4 bytes . Find the location of a[15][68]. Address(a[15][68]) = 0 + ((15 - 10) x (68 - 55 + 1) + (68 - 55)) x 4 = (5 x 14 + 13) x 4 = 83 x 4 = 332 answer </pre> <h3>By Column major order </h3> <p>If array is declared by a[m][n] where m is the number of rows while n is the number of columns, then address of an element a[i][j] of the array stored in row major order is calculated as, </p> <pre> Address(a[i][j]) = ((j*m)+i)*Size + BA </pre> <p>where BA is the base address of the array. </p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <pre> A [-5 ... +20][20 ... 70], BA = 1020, Size of element = 8 bytes. Find the location of a[0][30]. Address [A[0][30]) = ((30-20) x 24 + 5) x 8 + 1020 = 245 x 8 + 1020 = 2980 bytes </pre> <hr></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)></pre></3;i++)> unde, B. A. este adresa de bază sau adresa primului element al matricei a[0][0] .
Exemplu:
a[10...30, 55...75], base address of the array (BA) = 0, size of an element = 4 bytes . Find the location of a[15][68]. Address(a[15][68]) = 0 + ((15 - 10) x (68 - 55 + 1) + (68 - 55)) x 4 = (5 x 14 + 13) x 4 = 83 x 4 = 332 answer
După ordinea majoră a coloanei
Dacă matricea este declarată de a[m][n] unde m este numărul de rânduri în timp ce n este numărul de coloane, atunci adresa unui element a[i][j] din matricea stocată în ordinea majoră a rândurilor este calculată ca ,
Address(a[i][j]) = ((j*m)+i)*Size + BA
unde BA este adresa de bază a matricei.
limbajul de bază java
Exemplu:
A [-5 ... +20][20 ... 70], BA = 1020, Size of element = 8 bytes. Find the location of a[0][30]. Address [A[0][30]) = ((30-20) x 24 + 5) x 8 + 1020 = 245 x 8 + 1020 = 2980 bytes
