Cuvantul ' Încearcă 'este un extras din cuvânt' regăsire '. Trie este o structură de date sortată pe bază de arbore care stochează setul de șiruri. Are numărul de pointeri egal cu numărul de caractere ale alfabetului din fiecare nod. Poate căuta un cuvânt în dicționar cu ajutorul prefixului cuvântului. De exemplu, dacă presupunem că toate șirurile sunt formate din literele ' A ' la ' Cu ' în alfabetul englez, fiecare nod trie poate avea maximum 26 puncte.
șir de inversare java
Trie este cunoscut și sub numele de arbore digital sau arbore de prefix. Poziția unui nod în Trie determină cheia cu care este conectat acel nod.
Proprietățile Trie pentru un set de șir:
- Nodul rădăcină al trie reprezintă întotdeauna nodul nul.
- Fiecare copil al nodurilor este sortat alfabetic.
- Fiecare nod poate avea maximum 26 copii (de la A la Z).
- Fiecare nod (cu excepția rădăcinii) poate stoca o literă a alfabetului.
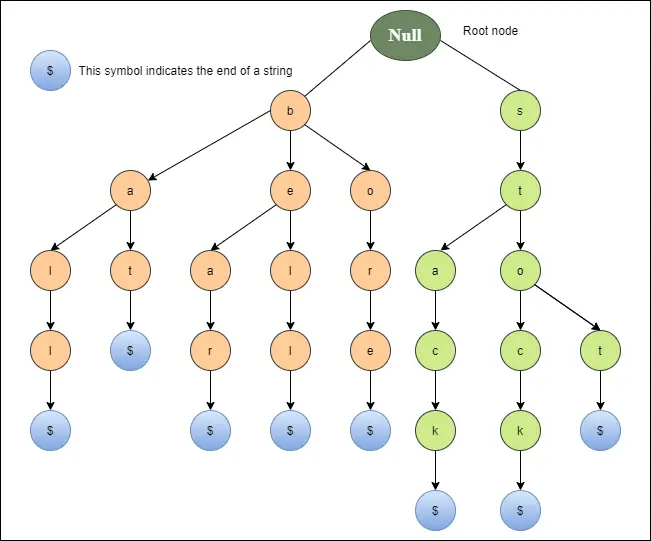
Diagrama de mai jos prezintă o reprezentare trie pentru clopot, urs, alez, liliac, minge, stop, stoc și stivă.
Operațiunile de bază ale lui Trie
Există trei operații în Trie:
- Inserarea unui nod
- Căutarea unui nod
- Ștergerea unui nod
Inserarea unui nod în Trie
Prima operație este să inserați un nou nod în trie. Înainte de a începe implementarea, este important să înțelegem câteva puncte:
- Fiecare literă a cheii de introducere (cuvânt) este inserată ca individ în Trie_node. Rețineți că copiii indică următorul nivel de noduri Trie.
- Matricea de caractere cheie acționează ca un index al copiilor.
- Dacă nodul prezent are deja o referință la litera prezentă, setați nodul prezent la acel nod referit. În caz contrar, creați un nou nod, setați litera să fie egală cu litera actuală și chiar începeți nodul prezent cu acest nou nod.
- Lungimea caracterului determină adâncimea încercării.
Implementarea inserării unui nou nod în Trie
public class Data_Trie { private Node_Trie root; public Data_Trie(){ this.root = new Node_Trie(); } public void insert(String word){ Node_Trie current = root; int length = word.length(); for (int x = 0; x <length; x++){ char l="word.charAt(x);" node_trie node="current.getNode().get(L);" if (node="=" null){ (); current.getnode().put(l, node); } current="node;" current.setword(true); < pre> <h3>Searching a node in Trie</h3> <p>The second operation is to search for a node in a Trie. The searching operation is similar to the insertion operation. The search operation is used to search a key in the trie. The implementation of the searching operation is shown below.</p> <p>Implementation of search a node in the Trie</p> <pre> class Search_Trie { private Node_Trie Prefix_Search(String W) { Node_Trie node = R; for (int x = 0; x <w.length(); x++) { char curletter="W.charAt(x);" if (node.containskey(curletter)) node="node.get(curLetter);" } else return null; node; public boolean search(string w) node_trie !="null" && node.isend(); < pre> <h3>Deletion of a node in the Trie</h3> <p>The Third operation is the deletion of a node in the Trie. Before we begin the implementation, it is important to understand some points:</p> <ol class="points"> <li>If the key is not found in the trie, the delete operation will stop and exit it.</li> <li>If the key is found in the trie, delete it from the trie.</li> </ol> <p> <strong>Implementation of delete a node in the Trie</strong> </p> <pre> public void Node_delete(String W) { Node_delete(R, W, 0); } private boolean Node_delete(Node_Trie current, String W, int Node_index) { if (Node_index == W.length()) { if (!current.isEndOfWord()) { return false; } current.setEndOfWord(false); return current.getChildren().isEmpty(); } char A = W.charAt(Node_index); Node_Trie node = current.getChildren().get(A); if (node == null) { return false; } boolean Current_Node_Delete = Node_delete(node, W, Node_index + 1) && !node.isEndOfWord(); if (Current_Node_Delete) { current.getChildren().remove(A); return current.getChildren().isEmpty(); } return false; } </pre> <h2>Applications of Trie</h2> <p> <strong>1. Spell Checker</strong> </p> <p>Spell checking is a three-step process. First, look for that word in a dictionary, generate possible suggestions, and then sort the suggestion words with the desired word at the top.</p> <p>Trie is used to store the word in dictionaries. The spell checker can easily be applied in the most efficient way by searching for words on a data structure. Using trie not only makes it easy to see the word in the dictionary, but it is also simple to build an algorithm to include a collection of relevant words or suggestions.</p> <p> <strong>2. Auto-complete</strong> </p> <p>Auto-complete functionality is widely used on text editors, mobile applications, and the Internet. It provides a simple way to find an alternative word to complete the word for the following reasons.</p> <ul> <li>It provides an alphabetical filter of entries by the key of the node.</li> <li>We trace pointers only to get the node that represents the string entered by the user.</li> <li>As soon as you start typing, it tries to complete your input.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>3. Browser history</strong> </p> <p>It is also used to complete the URL in the browser. The browser keeps a history of the URLs of the websites you've visited.</p> <h2>Advantages of Trie</h2> <ol class="points"> <li>It can be insert faster and search the string than hash tables and binary search trees.</li> <li>It provides an alphabetical filter of entries by the key of the node.</li> </ol> <h2>Disadvantages of Trie</h2> <ol class="points"> <li>It requires more memory to store the strings.</li> <li>It is slower than the hash table.</li> </ol> <h2>Complete program in C++</h2> <pre> #include #include #include #define N 26 typedef struct TrieNode TrieNode; struct TrieNode { char info; TrieNode* child[N]; int data; }; TrieNode* trie_make(char info) { TrieNode* node = (TrieNode*) calloc (1, sizeof(TrieNode)); for (int i = 0; i <n; i++) node → child[i]="NULL;" data="0;" info="info;" return node; } void free_trienode(trienode* node) { for(int i="0;" < n; if (node !="NULL)" free_trienode(node child[i]); else continue; free(node); trie loop start trienode* trie_insert(trienode* flag, char* word) temp="flag;" for (int word[i] ; int idx="(int)" - 'a'; (temp child[idx]="=" null) child[idx]; }trie flag; search_trie(trienode* position="word[i]" child[position]="=" 0; child[position]; && 1) 1; check_divergence(trienode* len="strlen(word);" (len="=" 0) last_index="0;" len; child[position]) j="0;" <n; j++) (j child[j]) + break; last_index; find_longest_prefix(trienode* (!word || word[0]="=" '�') null; longest_prefix="(char*)" calloc 1, sizeof(char)); longest_prefix[i]="word[i];" longest_prefix[len]="�" branch_idx="check_divergence(flag," longest_prefix) (branch_idx>= 0) { longest_prefix[branch_idx] = '�'; longest_prefix = (char*) realloc (longest_prefix, (branch_idx + 1) * sizeof(char)); } return longest_prefix; } int data_node(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { TrieNode* temp = flag; for (int i = 0; word[i]; i++) { int position = (int) word[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position]) { temp = temp → child[position]; } } return temp → data; } TrieNode* trie_delete(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { if (!flag) return NULL; if (!word || word[0] == '�') return flag; if (!data_node(flag, word)) { return flag; } TrieNode* temp = flag; char* longest_prefix = find_longest_prefix(flag, word); if (longest_prefix[0] == '�') { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } int i; for (i = 0; longest_prefix[i] != '�'; i++) { int position = (int) longest_prefix[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position] != NULL) { temp = temp → child[position]; } else { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } } int len = strlen(word); for (; i <len; i++) { int position="(int)" word[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position]) trienode* rm_node="temp→child[position];" temp child[position]="NULL;" free_trienode(rm_node); } free(longest_prefix); return flag; void print_trie(trienode* flag) (!flag) return; printf('%c ', temp→info); for (int i="0;" < n; print_trie(temp child[i]); search(trienode* flag, char* word) printf('search the word %s: word); (search_trie(flag, 0) printf('not found
'); else printf('found!
'); main() flag="trie_make('�');" 'oh'); 'way'); 'bag'); 'can'); search(flag, 'ohh'); 'ways'); print_trie(flag); printf('
'); printf('deleting 'hello'...
'); 'can'...
'); free_trienode(flag); 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Search the word ohh: Not Found Search the word bag: Found! Search the word can: Found! Search the word ways: Not Found Search the word way: Found! → h → e → l → l → o → w → a → y → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'hello'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'can'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g </pre> <hr></len;></n;></pre></w.length();></pre></length;> Aplicații ale lui Trie
1. Verificator ortografic
Verificarea ortografică este un proces în trei etape. Mai întâi, căutați acel cuvânt într-un dicționar, generați posibile sugestii și apoi sortați cuvintele sugestii cu cuvântul dorit în partea de sus.
localdate java
Trie este folosit pentru a stoca cuvântul în dicționare. Verificatorul ortografic poate fi aplicat cu ușurință în cel mai eficient mod prin căutarea cuvintelor pe o structură de date. Folosind trie nu numai că este ușor să vezi cuvântul în dicționar, dar este și simplu să construiești un algoritm care să includă o colecție de cuvinte sau sugestii relevante.
2. Completare automată
Funcționalitatea de completare automată este utilizată pe scară largă pe editorii de text, aplicațiile mobile și pe internet. Acesta oferă o modalitate simplă de a găsi un cuvânt alternativ pentru a completa cuvântul din următoarele motive.
- Oferă un filtru alfabetic al intrărilor după cheia nodului.
- Urmărim pointerii doar pentru a obține nodul care reprezintă șirul introdus de utilizator.
- De îndată ce începeți să tastați, încearcă să vă completeze introducerea.
3. Istoricul browserului
exemple de cod java
De asemenea, este folosit pentru a completa adresa URL în browser. Browserul păstrează un istoric al adreselor URL ale site-urilor web pe care le-ați vizitat.
Avantajele lui Trie
- Poate fi inserat mai rapid și poate căuta șirul decât tabelele hash și arborii binari de căutare.
- Oferă un filtru alfabetic al intrărilor după cheia nodului.
Dezavantajele lui Trie
- Este nevoie de mai multă memorie pentru a stoca șirurile.
- Este mai lent decât tabelul hash.
Program complet în C++
#include #include #include #define N 26 typedef struct TrieNode TrieNode; struct TrieNode { char info; TrieNode* child[N]; int data; }; TrieNode* trie_make(char info) { TrieNode* node = (TrieNode*) calloc (1, sizeof(TrieNode)); for (int i = 0; i <n; i++) node → child[i]="NULL;" data="0;" info="info;" return node; } void free_trienode(trienode* node) { for(int i="0;" < n; if (node !="NULL)" free_trienode(node child[i]); else continue; free(node); trie loop start trienode* trie_insert(trienode* flag, char* word) temp="flag;" for (int word[i] ; int idx="(int)" - \'a\'; (temp child[idx]="=" null) child[idx]; }trie flag; search_trie(trienode* position="word[i]" child[position]="=" 0; child[position]; && 1) 1; check_divergence(trienode* len="strlen(word);" (len="=" 0) last_index="0;" len; child[position]) j="0;" <n; j++) (j child[j]) + break; last_index; find_longest_prefix(trienode* (!word || word[0]="=" \'�\') null; longest_prefix="(char*)" calloc 1, sizeof(char)); longest_prefix[i]="word[i];" longest_prefix[len]="�" branch_idx="check_divergence(flag," longest_prefix) (branch_idx>= 0) { longest_prefix[branch_idx] = '�'; longest_prefix = (char*) realloc (longest_prefix, (branch_idx + 1) * sizeof(char)); } return longest_prefix; } int data_node(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { TrieNode* temp = flag; for (int i = 0; word[i]; i++) { int position = (int) word[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position]) { temp = temp → child[position]; } } return temp → data; } TrieNode* trie_delete(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { if (!flag) return NULL; if (!word || word[0] == '�') return flag; if (!data_node(flag, word)) { return flag; } TrieNode* temp = flag; char* longest_prefix = find_longest_prefix(flag, word); if (longest_prefix[0] == '�') { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } int i; for (i = 0; longest_prefix[i] != '�'; i++) { int position = (int) longest_prefix[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position] != NULL) { temp = temp → child[position]; } else { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } } int len = strlen(word); for (; i <len; i++) { int position="(int)" word[i] - \'a\'; if (temp → child[position]) trienode* rm_node="temp→child[position];" temp child[position]="NULL;" free_trienode(rm_node); } free(longest_prefix); return flag; void print_trie(trienode* flag) (!flag) return; printf(\'%c \', temp→info); for (int i="0;" < n; print_trie(temp child[i]); search(trienode* flag, char* word) printf(\'search the word %s: word); (search_trie(flag, 0) printf(\'not found
\'); else printf(\'found!
\'); main() flag="trie_make('�');" \'oh\'); \'way\'); \'bag\'); \'can\'); search(flag, \'ohh\'); \'ways\'); print_trie(flag); printf(\'
\'); printf(\'deleting \'hello\'...
\'); \'can\'...
\'); free_trienode(flag); 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Search the word ohh: Not Found Search the word bag: Found! Search the word can: Found! Search the word ways: Not Found Search the word way: Found! → h → e → l → l → o → w → a → y → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'hello'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'can'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g </pre> <hr></len;></n;> 