O matrice este o colecție omogenă de elemente de tip similar care au o locație de memorie contiguă.
O matrice este un tip de date definit de utilizator.
O matrice este un tip de structură de date în care stocăm elementele unui tip de date similar. Într-o matrice, putem stoca doar un set fix de elemente. Îl putem folosi și ca obiect.
Matricea este stocare bazată pe index, unde primul element este stocat la indexul 0. Structura de mai jos ajută la înțelegerea structurii unei matrice.
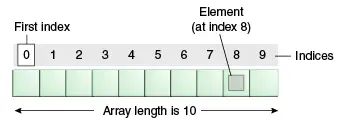
Caracteristicile unui Array
- O matrice stochează elemente care au același tip de date.
- Elemente de matrice stocate în locații de memorie adiacente.
- Stocarea elementelor de matrice 2-D este rânduită pe rând într-o locație de memorie adiacentă.
- Numele matricei reprezintă adresa elementului de pornire.
- Mărimea unui tablou ar trebui să fie inițializată în momentul declarației.
- Mărimea matricei ar trebui să fie o expresie constantă și nu o variabilă.
- Putem prelua elemente de matrice specificând valoarea indexului corespunzătoare elementului.
Avantaj
Optimizarea codului: O matrice ajută la optimizarea codului, ceea ce crește viteza și performanța programului. Ne permite să extragem sau să sortăm datele matricei mai eficient.
Acces aleator: Oferă posibilitatea de a accesa orice date dintr-o matrice în timp constant (independent de poziția și dimensiunea acesteia). Astfel, putem obține orice date dintr-o matrice situată în orice poziție de index direct.
Dezavantaj
Limita de dimensiune: O matrice ne permite să stocăm doar un număr fix de elemente. Odată ce matricea este declarată, nu-i putem modifica dimensiunea. Prin urmare, dacă dorim să inserăm mai mult element decât este declarat, nu este posibil.
Declarație de matrice
La fel ca JavaScript, TypeScript acceptă și matrice. Există două moduri de a declara o matrice:
1. Folosind paranteze drepte.
let array_name[:datatype] = [val1,val2,valn..]
Exemplu:
let fruits: string[] = ['Apple', 'Orange', 'Banana'];
2. Folosind un tip de matrice generic.
cum să dereferiți un indicator în c
let array_name: Array = [val1,val2,valn..]
Exemplu:
let fruits: Array = ['Apple', 'Orange', 'Banana'];
Tipuri de matrice în TypeScript
Există două tipuri de matrice:
- Matrice unidimensională
- Matrice multidimensională

Matrice unidimensională
O matrice unidimensională este un tip de matrice liniară, care conține un singur rând pentru stocarea datelor. Are un singur set de paranteze pătrate ('[]'). Putem accesa elementele sale folosind indexul de rând sau coloană.
Sintaxă
let array_name[:datatype];
Inițializare
array_name = [val1,val2,valn..]
Exemplu
let arr:number[]; arr = [1, 2, 3, 4] console.log('Array[0]: ' +arr[0]); console.log('Array[1]: ' +arr[1]);
Ieșire:
Array[0]: 1 Array[1]: 2
Matrice multidimensională
O matrice multidimensională este o matrice care conține una sau mai multe matrice. În matricea multidimensională, datele sunt stocate într-un index bazat pe rând și coloane (cunoscut și ca formă de matrice). O matrice bidimensională (matrice 2-D) este cea mai simplă formă a unei matrice multidimensionale.

Sintaxă
let arr_name:datatype[][] = [ [a1,a2,a3], [b1,b2,b3] ];
Inițializare
let arr_name:datatype[initial_array_index][referenced_array_index] = [ [val1,val2,val 3], [v1,v2,v3]];
Exemplu
var mArray:number[][] = [[1,2,3],[5,6,7]] ; console.log(mArray[0][0]); console.log(mArray[0][1]); console.log(mArray[0][2]); console.log(); console.log(mArray[1][0]); console.log(mArray[1][1]); console.log(mArray[1][2]);
Ieșire:
1 2 3 5 6 7
Obiect matrice
Obiectele matrice ne permit să stocăm mai multe valori într-o singură variabilă. Putem crea o matrice folosind obiectul Array. Constructorul Array este folosit pentru a transmite următoarele argumente pentru crearea matricei.
- O valoare numerică care reprezintă dimensiunea unui tablou sau
- O listă de valori separate prin virgulă.
Sintaxă
let arr_name:datatype[] = new Array(values);
Exemplu
//array by using the Array object. let arr:string[] = new Array('JavaTpoint','2200','Java','Abhishek'); for(var i = 0;i <arr.length;i++) { console.log(arr[i]); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> JavaTpoint 2200 Java Abhishek </pre> <h3>Array Traversal by using a for...in loop</h3> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <pre> let i:any; let arr:string[] = ['JavaTpoint', '2300', 'Java', 'Abhishek']; for(i in arr) { console.log(arr[i]) } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> JavaTpoint 2300 Java Abhishek </pre> <h3>Passing Arrays to Functions</h3> <p>We can pass arrays to functions by specifying the array name without an index.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <pre> let arr:string[] = new Array('JavaTpoint', '2300', 'Java', 'Abhishek'); //Passing arrays in function function display(arr_values:string[]) { for(let i = 0;i <arr_values.length;i++) { console.log(arr[i]); } calling arrays in function display(arr); < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> JavaTpoint 2300 Java Abhishek </pre> <hr> <h2>TypeScript Spread operator</h2> <p>The spread operator is used to initialize arrays and objects from another array or object. We can also use it for object de-structuring. It is a part of the ES 6 version.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <pre> let arr1 = [ 1, 2, 3]; let arr2 = [ 4, 5, 6]; //Create new array from existing array let copyArray = [...arr1]; console.log('CopiedArray: ' +copyArray); //Create new array from existing array with more elements let newArray = [...arr1, 7, 8]; console.log('NewArray: ' +newArray); //Create array by merging two arrays let mergedArray = [...arr1, ...arr2]; console.log('MergedArray: ' +mergedArray); </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> CopiedArray: 1,2,3 NewArray: 1,2,3,7,8 MergedArray: 1,2,3,4,5,6 </pre> <hr> <h2>Array Methods</h2> <p>The list of array methods with their description is given below.</p> <table class="table"> <tr> <th>SN</th> <th>Method</th> <th>Description</th> </tr> <tr> <td>1.</td> <td>concat()</td> <td>It is used to joins two arrays and returns the combined result.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>2.</td> <td>copyWithin()</td> <td>It copies a sequence of an element within the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>3.</td> <td>every()</td> <td>It returns true if every element in the array satisfies the provided testing function.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>4.</td> <td>fill()</td> <td>It fills an array with a static value from the specified start to end index.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>5.</td> <td>indexOf()</td> <td>It returns the index of the matching element in the array, otherwise -1.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>6.</td> <td>includes()</td> <td>It is used to check whether the array contains a certain element or not.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>7.</td> <td>Join()</td> <td>It is used to joins all elements of an array into a string.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>8.</td> <td>lastIndexOf()</td> <td>It returns the last index of an element in the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>9.</td> <td>Pop()</td> <td>It is used to removes the last elements of the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>10.</td> <td>Push()</td> <td>It is used to add new elements to the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>11.</td> <td>reverse()</td> <td>It is used to reverse the order of an element in the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>12.</td> <td>Shift()</td> <td>It is used to removes and returns the first element of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>13.</td> <td>slice()</td> <td>It returns the section fo an array in the new array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>14.</td> <td>sort()</td> <td>It is used to sort the elements of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>15.</td> <td>splice()</td> <td>It is used to add or remove the elements from an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>16.</td> <td>toString()</td> <td>It returns the string representation of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>17.</td> <td>unshift()</td> <td>It is used to add one or more elements to the beginning of an array.</td> </tr> </table></arr_values.length;i++)></pre></arr.length;i++)> Array Traversal folosind o buclă for...in
Exemplu
let i:any; let arr:string[] = ['JavaTpoint', '2300', 'Java', 'Abhishek']; for(i in arr) { console.log(arr[i]) } Ieșire:
JavaTpoint 2300 Java Abhishek
Transmiterea de tablouri la funcții
Putem trece matrice la funcții prin specificarea numelui matricei fără un index.
Exemplu
cum se convertesc un întreg în șir de caractere java
let arr:string[] = new Array('JavaTpoint', '2300', 'Java', 'Abhishek'); //Passing arrays in function function display(arr_values:string[]) { for(let i = 0;i <arr_values.length;i++) { console.log(arr[i]); } calling arrays in function display(arr); < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> JavaTpoint 2300 Java Abhishek </pre> <hr> <h2>TypeScript Spread operator</h2> <p>The spread operator is used to initialize arrays and objects from another array or object. We can also use it for object de-structuring. It is a part of the ES 6 version.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <pre> let arr1 = [ 1, 2, 3]; let arr2 = [ 4, 5, 6]; //Create new array from existing array let copyArray = [...arr1]; console.log('CopiedArray: ' +copyArray); //Create new array from existing array with more elements let newArray = [...arr1, 7, 8]; console.log('NewArray: ' +newArray); //Create array by merging two arrays let mergedArray = [...arr1, ...arr2]; console.log('MergedArray: ' +mergedArray); </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> CopiedArray: 1,2,3 NewArray: 1,2,3,7,8 MergedArray: 1,2,3,4,5,6 </pre> <hr> <h2>Array Methods</h2> <p>The list of array methods with their description is given below.</p> <table class="table"> <tr> <th>SN</th> <th>Method</th> <th>Description</th> </tr> <tr> <td>1.</td> <td>concat()</td> <td>It is used to joins two arrays and returns the combined result.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>2.</td> <td>copyWithin()</td> <td>It copies a sequence of an element within the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>3.</td> <td>every()</td> <td>It returns true if every element in the array satisfies the provided testing function.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>4.</td> <td>fill()</td> <td>It fills an array with a static value from the specified start to end index.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>5.</td> <td>indexOf()</td> <td>It returns the index of the matching element in the array, otherwise -1.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>6.</td> <td>includes()</td> <td>It is used to check whether the array contains a certain element or not.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>7.</td> <td>Join()</td> <td>It is used to joins all elements of an array into a string.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>8.</td> <td>lastIndexOf()</td> <td>It returns the last index of an element in the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>9.</td> <td>Pop()</td> <td>It is used to removes the last elements of the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>10.</td> <td>Push()</td> <td>It is used to add new elements to the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>11.</td> <td>reverse()</td> <td>It is used to reverse the order of an element in the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>12.</td> <td>Shift()</td> <td>It is used to removes and returns the first element of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>13.</td> <td>slice()</td> <td>It returns the section fo an array in the new array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>14.</td> <td>sort()</td> <td>It is used to sort the elements of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>15.</td> <td>splice()</td> <td>It is used to add or remove the elements from an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>16.</td> <td>toString()</td> <td>It returns the string representation of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>17.</td> <td>unshift()</td> <td>It is used to add one or more elements to the beginning of an array.</td> </tr> </table></arr_values.length;i++)> Operatorul Spread TypeScript
Operatorul de răspândire este folosit pentru a inițializa matrice și obiecte dintr-un alt tablou sau obiect. Îl putem folosi și pentru destructurarea obiectelor. Face parte din versiunea ES 6.
Exemplu
let arr1 = [ 1, 2, 3]; let arr2 = [ 4, 5, 6]; //Create new array from existing array let copyArray = [...arr1]; console.log('CopiedArray: ' +copyArray); //Create new array from existing array with more elements let newArray = [...arr1, 7, 8]; console.log('NewArray: ' +newArray); //Create array by merging two arrays let mergedArray = [...arr1, ...arr2]; console.log('MergedArray: ' +mergedArray);
Ieșire:
CopiedArray: 1,2,3 NewArray: 1,2,3,7,8 MergedArray: 1,2,3,4,5,6
Metode de matrice
Lista metodelor matrice cu descrierea lor este dată mai jos.
| SN | Metodă | Descriere |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | concat() | Este folosit pentru a uni două matrice și returnează rezultatul combinat. |
| 2. | copyWithin() | Copiază o secvență a unui element din matrice. |
| 3. | fiecare() | Returnează adevărat dacă fiecare element din matrice satisface funcția de testare furnizată. |
| 4. | completati() | Umple o matrice cu o valoare statică de la indexul specificat de la început până la sfârșit. |
| 5. | Index de() | Returnează indexul elementului care se potrivește din matrice, în caz contrar -1. |
| 6. | include () | Este folosit pentru a verifica dacă matricea conține un anumit element sau nu. |
| 7. | A te alatura() | Este folosit pentru a uni toate elementele unui tablou într-un șir. |
| 8. | lastIndexOf() | Returnează ultimul index al unui element din matrice. |
| 9. | Pop() | Este folosit pentru a elimina ultimele elemente ale matricei. |
| 10. | Apăsaţi() | Este folosit pentru a adăuga elemente noi la matrice. |
| unsprezece. | verso() | Este folosit pentru a inversa ordinea unui element din matrice. |
| 12. | Schimb() | Este folosit pentru a elimina și returna primul element al unui tablou. |
| 13. | felie() | Returnează secțiunea pentru o matrice din noua matrice. |
| 14. | fel() | Este folosit pentru a sorta elementele unui tablou. |
| cincisprezece. | lipitură() | Este folosit pentru a adăuga sau elimina elemente dintr-o matrice. |
| 16. | toString() | Returnează reprezentarea în șir a unui tablou. |
| 17. | unshift() | Este folosit pentru a adăuga unul sau mai multe elemente la începutul unui tablou. |
