Instrucțiunea IF este o parte a funcției fluxului de control din SQL Server. De obicei, este o declarație de luare a deciziilor în diferite limbaje de programare care returnează o valoare bazată pe condițiile date . Această instrucțiune execută codul scris în blocul IF când condiția dată este evaluată ca adevărată și când condiția este falsă, atunci instrucțiunea ELSE va fi executată.
Declarația IF
Următoarele sunt sintaxa care ilustrează utilizarea acestei instrucțiuni în SQL Server:
IF boolean_expression BEGIN { statement_block } END În sintaxa de mai sus, statement_block în ÎNCEPE... Sfârșit blocul este executat atunci când expresie_booleană este mulțumit de condiție. În caz contrar, acest bloc este omis, iar controlul programului este mutat în instrucțiunea după Sfârşit cuvânt cheie. Ar trebui să știm că dacă expresia conține a SELECTAȚI declarație, trebuie includeți-le între paranteze .
Exemplu
Să vedem exemplul pentru a înțelege instrucțiunea IF fără blocul ELSE. Exemplul de mai jos va afișa rezultatul când condiția este îndeplinită. În caz contrar, controlul programului s-a mutat în instrucțiunea după cuvântul cheie END, dacă există.
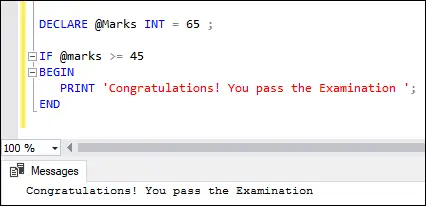
DECLARE @Marks INT = 65 ; IF @marks >= 45 BEGIN PRINT 'Congratulations! You pass the Examination'; END
Executarea instrucțiunii va da rezultatul de mai jos:
Acum, o vom demonstra mai jos ' Student' tabel cu următoarele date:

Mai jos este un alt exemplu care primește note totale a unui student selectat din ' Student' tabel în baza de date eșantion și apoi tipărește a mesaj dacă este mai mare de 400 .
BEGIN DECLARE @Total_Marks INT; SELECT @Total_Marks = total_marks FROM Student WHERE age>25; SELECT @Total_Marks; IF @Total_Marks > 400 BEGIN PRINT 'Congratulations! You pass the Examination'; END END
Vom obține rezultatul de mai jos:

Dacă vrem să vedem mesajul de ieșire de mai sus, ar trebui să facem clic pe Mesaje fila:

Declarația IF-ELSE
În scenariul real, trebuie să efectuăm o acțiune ori de câte ori condiția din instrucțiunea IF este TRUE sau FALSE. În acest caz, instrucțiunea IF...ELSE este utilă. Această instrucțiune execută blocul de instrucțiuni ELSE atunci când condiția din clauza IF este evaluată FALS.
Următoarele sunt sintaxa care ilustrează utilizarea instrucțiunii IF ELSE în SQL Server :
IF expression BEGIN Statement block -- It executes when the IF clause expression is TRUE. END ELSE BEGIN Statement block -- It executes when the IF clause expression is FALSE. END
Exemplu
Să vedem exemplul pentru a înțelege instrucțiunea IF cu blocul ELSE. Exemplul de mai jos va afișa mesajul „ Felicitări! Treci Examenul ' când condiția IF este îndeplinită. În caz contrar, afișați „ Ai eșuat! Mai mult noroc data viitoare '.
DECLARE @Marks INT; SET @Marks = 65; IF @marks <45 begin print 'congratulations! you pass the examination'; end else 'you are failed! better luck next time'; < pre> <p>Executing the statement will give the below output. Here, the <strong>marks</strong> variable is <strong>65</strong> , and the <strong>condition (65<45)< strong> is not satisfied. Therefore, the message inside the ELSE block is displayed:</45)<></strong></p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/49/sql-server-if-else-5.webp" alt="SQL Server IF ELSE"> <p>We will get this output because the condition <strong>(65>45)</strong> is satisfied. Therefore, the message inside the IF block is displayed:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/49/sql-server-if-else-6.webp" alt="SQL Server IF ELSE"> <p>Now, we will demonstrate the IF ELSE statement on the above ' <strong>Student'</strong> table. In this example, we are going to check whether the student <strong>total marks</strong> is <strong>greater than or equal to 400</strong> or not as follows:</p> <ul> <li>When the IF condition is TRUE, we will get the student records whose total marks are greater than or equal to 550.</li> <li>If the condition is FALSE, we will get the student records whose total marks are less than 550.</li> </ul> <p>Here is the program:</p> <pre> DECLARE @Marks INT; SET @Marks = 600 ; IF @Marks >= 550 BEGIN SELECT id, name, gender, age, total_marks FROM Student WHERE total_marks >= 550 ORDER BY age ASC END ELSE BEGIN SELECT id, name, gender, age, total_marks FROM Student WHERE total_marks <550 order by age asc end < pre> <p>In this code, we have specified the <strong>@Marks</strong> variable to <strong>600</strong> , and the condition (600 >= 550) is satisfied. Therefore, we will get the output where student records whose total marks are greater than or equal to 550 are displayed.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/49/sql-server-if-else-7.webp" alt="SQL Server IF ELSE"> <p>If we changed the <strong>@Marks</strong> variable to <strong>500</strong> and the condition (500 >= 550) becomes false. Therefore, we will get the output where student records whose total marks are less than 550 are displayed.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/49/sql-server-if-else-8.webp" alt="SQL Server IF ELSE"> <h2>Nested IF ELSE Statement</h2> <p>Unlike other programming languages, we can nest an IF...ELSE statement inside another IF...ELSE statement in SQL Server. Let us demonstrate it with the following example:</p> <pre> DECLARE @age INT; SET @age = 6; IF @age <18 50 print 'you are underage'; else begin if @age < below 50'; senior cetizen'; end; pre> <p>In this example, we are going to check whether the <strong>age is underage, below 50, or senior citizen</strong> as follows:</p> <ul> <li>If the value of the <strong>@age</strong> variable is below <strong>18</strong> , it will print the person is <strong>underage</strong> .</li> <li>If the condition is FALSE, the ELSE part will be executed that has a nested IF…ELSE.</li> <li>If the value of the <strong>@age</strong> variable is under <strong>50</strong> , it will print <strong>below 50</strong> . Finally, if no condition is satisfied, it will print <strong>senior citizens</strong> .</li> </ul> <p>Here is the result:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/49/sql-server-if-else-9.webp" alt="SQL Server IF ELSE"> <p>This article gives a complete overview of how to use the SQL Server IF ELSE statement. Here we have learned:</p> <ul> <li>Variables are objects that serve as placeholders.</li> <li>The keyword BEGIN will be used to start a statement block, and the END keyword must be used to close it.</li> <li>The use of ELSE in an IF... ELSE statement is optional.</li> <li>It's also possible to nest an IF...ELSE statement inside another IF...ELSE statement. However, nesting an IF statement within another statement is bad practice because it makes the code difficult to read and maintain.</li> </ul> <hr></18></pre></550></pre></45>
