A Max-Heap este un arbore binar complet în care valoarea din fiecare nod intern este mai mare sau egală cu valorile din copiii acelui nod. Maparea elementelor unui heap într-o matrice este trivială: dacă un nod este stocat un index k, atunci copilul său din stânga este stocat la index 2k+1 și copilul său drept la index 2k+2 .
Exemple de Max Heap:
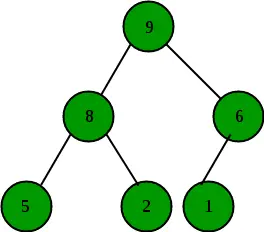
Cum este reprezentat Max Heap?
Un maxim Heap este un arbore binar complet. Un heap maxim este de obicei reprezentat ca o matrice. Elementul rădăcină va fi la Arr[0]. Tabelul de mai jos prezintă indici ai altor noduri pentru al-lea nod, adică Arr[i]:
- Arr[(i-1)/2] Returnează nodul părinte.
- Arr[(2*i)+1] Returnează nodul copil stâng.
- Arr[(2*i)+2] Returnează nodul secundar corect.
Operațiuni pe Max Heap:
- getMax() : returnează elementul rădăcină din Max Heap. Timpul Complexitatea acestei operațiuni este O(1) .
- extractMax() : elimină elementul maxim din MaxHeap. Timpul Complexitatea acestei operațiuni este O(log n) deoarece această operație trebuie să mențină proprietatea heap (prin apelarea heapify()) după eliminarea rădăcinii.
- introduce() : Introducerea unei noi chei ia O(log n) timp. Adăugăm o cheie nouă la capătul arborelui. Dacă noua cheie este mai mică decât cea părinte, atunci nu trebuie să facem nimic. În caz contrar, trebuie să traversăm în sus pentru a remedia proprietatea heap încălcată.
Notă: În implementarea de mai jos, facem indexare din indexul 1 pentru a simplifica implementarea.
Piton
lista de fonturi din gimp
# Python3 implementation of Max Heap> import> sys> class> MaxHeap:> >def> __init__(>self>, maxsize):> > >self>.maxsize>=> maxsize> >self>.size>=> 0> >self>.Heap>=> [>0>]>*> (>self>.maxsize>+> 1>)> >self>.Heap[>0>]>=> sys.maxsize> >self>.FRONT>=> 1> ># Function to return the position of> ># parent for the node currently> ># at pos> >def> parent(>self>, pos):> > >return> pos>/>/> 2> ># Function to return the position of> ># the left child for the node currently> ># at pos> >def> leftChild(>self>, pos):> > >return> 2> *> pos> ># Function to return the position of> ># the right child for the node currently> ># at pos> >def> rightChild(>self>, pos):> > >return> (>2> *> pos)>+> 1> ># Function that returns true if the passed> ># node is a leaf node> >def> isLeaf(>self>, pos):> > >if> pos>>>>self>.size>/>/>2>)>and> pos <>=> self>.size:> >return> True> >return> False> ># Function to swap two nodes of the heap> >def> swap(>self>, fpos, spos):> > >self>.Heap[fpos],>self>.Heap[spos]>=> (>self>.Heap[spos],> >self>.Heap[fpos])> ># Function to heapify the node at pos> >def> maxHeapify(>self>, pos):> ># If the node is a non-leaf node and smaller> ># than any of its child> >if> not> self>.isLeaf(pos):> >if> (>self>.Heap[pos] <>self>.Heap[>self>.leftChild(pos)]>or> >self>.Heap[pos] <>self>.Heap[>self>.rightChild(pos)]):> ># Swap with the left child and heapify> ># the left child> >if> (>self>.Heap[>self>.leftChild(pos)]>>>> .Heap[>self>.rightChild(pos)]):> >self>.swap(pos,>self>.leftChild(pos))> >self>.maxHeapify(>self>.leftChild(pos))> ># Swap with the right child and heapify> ># the right child> >else>:> >self>.swap(pos,>self>.rightChild(pos))> >self>.maxHeapify(>self>.rightChild(pos))> ># Function to insert a node into the heap> >def> insert(>self>, element):> > >if> self>.size>>>>.maxsize:> >return> >self>.size>+>=> 1> >self>.Heap[>self>.size]>=> element> >current>=> self>.size> >while> (>self>.Heap[current]>>>> .Heap[>self>.parent(current)]):> >self>.swap(current,>self>.parent(current))> >current>=> self>.parent(current)> ># Function to print the contents of the heap> >def> Print>(>self>):> > >for> i>in> range>(>1>, (>self>.size>/>/> 2>)>+> 1>):> >print>(>'PARENT : '> +> str>(>self>.Heap[i])>+> >'LEFT CHILD : '> +> str>(>self>.Heap[>2> *> i])>+> >'RIGHT CHILD : '> +> str>(>self>.Heap[>2> *> i>+> 1>]))> ># Function to remove and return the maximum> ># element from the heap> >def> extractMax(>self>):> >popped>=> self>.Heap[>self>.FRONT]> >self>.Heap[>self>.FRONT]>=> self>.Heap[>self>.size]> >self>.size>->=> 1> >self>.maxHeapify(>self>.FRONT)> > >return> popped> # Driver Code> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> > >print>(>'The maxHeap is '>)> > >maxHeap>=> MaxHeap(>15>)> >maxHeap.insert(>5>)> >maxHeap.insert(>3>)> >maxHeap.insert(>17>)> >maxHeap.insert(>10>)> >maxHeap.insert(>84>)> >maxHeap.insert(>19>)> >maxHeap.insert(>6>)> >maxHeap.insert(>22>)> >maxHeap.insert(>9>)> >maxHeap.>Print>()> > >print>(>'The Max val is '> +> str>(maxHeap.extractMax()))> |
>
împărțirea șirurilor de caractere c++
>
plsqlIeșire
The maxHeap is PARENT : 84LEFT CHILD : 22RIGHT CHILD : 19 PARENT : 22LEFT CHILD : 17RIGHT CHILD : 10 PARENT : 19LEFT CHILD : 5RIGHT CHILD : 6 PARENT : 17LEFT CHILD : 3RIGHT CHILD : 9 The Max val is 84>
Utilizarea funcțiilor Bibliotecii:
Folosim heapq clasă pentru a implementa Heap în Python. În mod implicit, Min Heap este implementat de această clasă. Dar înmulțim fiecare valoare cu -1, astfel încât să o putem folosi ca MaxHeap.
Python3
Java șir înlocuiește toate
# Python3 program to demonstrate working of heapq> from> heapq>import> heappop, heappush, heapify> # Creating empty heap> heap>=> []> heapify(heap)> # Adding items to the heap using heappush> # function by multiplying them with -1> heappush(heap,>->1> *> 10>)> heappush(heap,>->1> *> 30>)> heappush(heap,>->1> *> 20>)> heappush(heap,>->1> *> 400>)> # printing the value of maximum element> print>(>'Head value of heap : '> +> str>(>->1> *> heap[>0>]))> # printing the elements of the heap> print>(>'The heap elements : '>)> for> i>in> heap:> >print>((>->1>*>i), end>=>' '>)> print>(>'
'>)> element>=> heappop(heap)> # printing the elements of the heap> print>(>'The heap elements : '>)> for> i>in> heap:> >print>(>->1> *> i, end>=> ' '>)> |
>
>Ieșire
Head value of heap : 400 The heap elements : 400 30 20 10 The heap elements : 30 10 20>
Utilizarea funcțiilor Bibliotecă cu metoda dunder pentru numere, șiruri, tupluri, obiecte etc
Folosim heapq clasă pentru a implementa Heaps în Python. În mod implicit, Min Heap este implementat de această clasă.
Pentru a implementa MaxHeap nu limitându-ne doar la numere, ci la orice tip de obiect (String, Tuple, Object etc) ar trebui să
- Creați o clasă Wrapper pentru elementul din listă.
- Ignorați __lt__ metoda dunder pentru a da rezultat invers.
În continuare este implementarea metodei menționate aici.
java sortarea unei liste de matrice
Python3
'''> Python3 program to implement MaxHeap Operation> with built-in module heapq> for String, Numbers, Objects> '''> from> functools>import> total_ordering> import> heapq>|_+_| |
