Dat un simplu arbore de expresie constând din operatori binari de bază, adică + - * și / și unele numere întregi evaluează arborele de expresie.
Exemple:
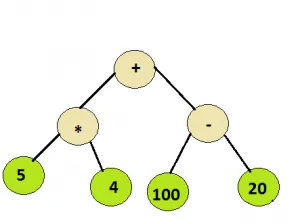
Practică recomandată Arborele de expresie Încearcă!Intrare: Nodul rădăcină al arborelui de mai jos
Ieșire: 100
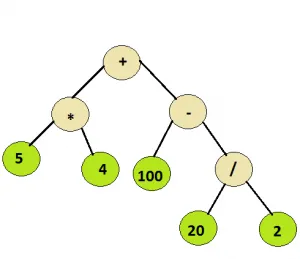
Intrare: Nodul rădăcină al arborelui de mai jos
un exemplu de sistem open source este
Ieșire: 110
Abordare: Abordarea pentru rezolvarea acestei probleme se bazează pe următoarele observații:
Deoarece toți operatorii din arbore sunt binari, fiecare nod va avea fie 0, fie 2 copii. După cum se poate deduce din exemplele de mai sus, valorile întregi ar apărea la nodurile frunză, în timp ce nodurile interioare reprezintă operatorii.
Prin urmare, putem face parcurgerea în ordine a arborelui binar și evaluăm expresia pe măsură ce avansăm.
Pentru a evalua arborele de sintaxă poate fi urmată o abordare recursivă.
Algoritm:
- Fie t arborele de sintaxă
- Dacă t nu este nul, atunci
- Dacă t.info este operand atunci
- Reveniți t.info
- Altfel
- A = rezolva (t.stânga)
- B = rezolva (t.dreapta)
- return A operator B unde operator este informația conținută în t
Mai jos este implementarea abordării de mai sus:
C++// C++ program to evaluate an expression tree #include
// Java program to evaluate expression tree import java.lang.*; class GFG{ Node root; // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree public static class Node { String data; Node left right; Node(String d) { data = d; left = null; right = null; } } private static int toInt(String s) { int num = 0; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate // the number normally if (s.charAt(0) != '-') for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) num = num * 10 + ((int)s.charAt(i) - 48); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for(int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++) num = num * 10 + ((int)(s.charAt(i)) - 48); num = num * -1; } return num; } // This function receives a node of the syntax // tree and recursively evaluate it public static int evalTree(Node root) { // Empty tree if (root == null) return 0; // Leaf node i.e an integer if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return toInt(root.data); // Evaluate left subtree int leftEval = evalTree(root.left); // Evaluate right subtree int rightEval = evalTree(root.right); // Check which operator to apply if (root.data.equals('+')) return leftEval + rightEval; if (root.data.equals('-')) return leftEval - rightEval; if (root.data.equals('*')) return leftEval * rightEval; return leftEval / rightEval; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a sample tree Node root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('-4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('20'); System.out.println(evalTree(root)); root = null; // Creating a sample tree root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('/'); root.right.right.left = new Node('20'); root.right.right.right = new Node('2'); System.out.println(evalTree(root)); } } // This code is contributed by Ankit Gupta
# Python program to evaluate expression tree # Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree class node: def __init__(self value): self.left = None self.data = value self.right = None # This function receives a node of the syntax tree # and recursively evaluate it def evaluateExpressionTree(root): # empty tree if root is None: return 0 # leaf node if root.left is None and root.right is None: return int(root.data) # evaluate left tree left_sum = evaluateExpressionTree(root.left) # evaluate right tree right_sum = evaluateExpressionTree(root.right) # check which operation to apply if root.data == '+': return left_sum + right_sum elif root.data == '-': return left_sum - right_sum elif root.data == '*': return left_sum * right_sum else: return left_sum // right_sum # Driver function to test above problem if __name__ == '__main__': # creating a sample tree root = node('+') root.left = node('*') root.left.left = node('5') root.left.right = node('-4') root.right = node('-') root.right.left = node('100') root.right.right = node('20') print (evaluateExpressionTree(root)) root = None # creating a sample tree root = node('+') root.left = node('*') root.left.left = node('5') root.left.right = node('4') root.right = node('-') root.right.left = node('100') root.right.right = node('/') root.right.right.left = node('20') root.right.right.right = node('2') print (evaluateExpressionTree(root)) # This code is contributed by Harshit Sidhwa
// C# program to evaluate expression tree using System; public class GFG { // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree public class Node { public String data; public Node left right; public Node(String d) { data = d; left = null; right = null; } } private static int toInt(String s) { int num = 0; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate // the number normally if (s[0] != '-') for (int i = 0; i < s.Length; i++) num = num * 10 + ((int) s[i] - 48); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for (int i = 1; i < s.Length; i++) num = num * 10 + ((int) (s[i]) - 48); num = num * -1; } return num; } // This function receives a node of the syntax // tree and recursively evaluate it public static int evalTree(Node root) { // Empty tree if (root == null) return 0; // Leaf node i.e an integer if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return toInt(root.data); // Evaluate left subtree int leftEval = evalTree(root.left); // Evaluate right subtree int rightEval = evalTree(root.right); // Check which operator to apply if (root.data.Equals('+')) return leftEval + rightEval; if (root.data.Equals('-')) return leftEval - rightEval; if (root.data.Equals('*')) return leftEval * rightEval; return leftEval / rightEval; } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { // Creating a sample tree Node root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('-4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('20'); Console.WriteLine(evalTree(root)); root = null; // Creating a sample tree root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('/'); root.right.right.left = new Node('20'); root.right.right.right = new Node('2'); Console.WriteLine(evalTree(root)); } } // This code is contributed by umadevi9616
<script> // javascript program to evaluate expression tree var root; // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } function toInt( s) { var num = 0; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate // the number normally if (s.charAt(0) != '-') for (i = 0; i < s.length; i++) num = num * 10 + ( s.charCodeAt(i) - 48); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for (i = 1; i < s.length; i++) num = num * 10 + (s.charCodeAt(i) - 48); num = num * -1; } return num; } // This function receives a node of the syntax // tree and recursively evaluate it function evalTree(root) { // Empty tree if (root == null) return 0; // Leaf node i.e an integer if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return toInt(root.data); // Evaluate left subtree var leftEval = evalTree(root.left); // Evaluate right subtree var rightEval = evalTree(root.right); // Check which operator to apply if (root.data === ('+')) return leftEval + rightEval; if (root.data === ('-')) return leftEval - rightEval; if (root.data === ('*')) return leftEval * rightEval; return leftEval / rightEval; } // Driver code // Creating a sample tree var root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('-4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('20'); document.write(evalTree(root)); root = null; // Creating a sample tree root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('/'); root.right.right.left = new Node('20'); root.right.right.right = new Node('2'); document.write('
'+evalTree(root)); // This code is contributed by gauravrajput1 </script>
Ieșire
60 110
Complexitatea timpului: O(n) deoarece fiecare nod este vizitat o dată.
Spațiu auxiliar: Pe)